

The most effective way to resolve pinch valve issues is to identify the root cause early—whether it’s sleeve wear, actuation failure, or leaks—and apply targeted troubleshooting steps to restore performance.
Pinch valves are favored for their durability and simplicity in handling slurries, abrasive materials, and corrosive fluids.
But like any component, they can develop problems over time.
By understanding how to recognize and troubleshoot these issues, operators can extend the life of the valve and avoid costly system downtime.
This guide to pinch valve troubleshooting outlines the most common issues, their causes, and practical steps to fix or prevent them.
A common pinch valve problem is that the sleeve doesn’t fully open or close. This can lead to reduced flow or failure to stop the fluid entirely.
Possible Causes:
Troubleshooting Steps:
If the issue persists after checking these factors, consider replacing the sleeve or consulting with the pinch valve supplier to assess whether a different model is more appropriate for the application.
Pinch valves are known for their tight shut-off capability. If you notice leaks, especially when the valve is closed, the most likely culprit is the sleeve.
Possible Causes:
Pinch Valve Troubleshooting Tip:
In pneumatic pinch valves, proper operation depends on maintaining consistent air pressure. If the valve isn’t responding properly or is slow to actuate, there may be an air pressure issue.
Possible Causes:
Troubleshooting Tips:
Regularly scheduled checks on your pneumatic control system will help maintain consistent valve function and prevent unexpected actuation failures.
Sleeve wear is a normal part of pinch valve operation, but if it’s happening too frequently, it’s a sign that the system conditions may be putting undue stress on the sleeve.
Common Causes:
Pinch Valve Troubleshooting Tip:
Many pinch valve manufacturers offer specialized sleeves for different conditions, such as natural rubber for general abrasion or EPDM for chemical resistance.
Unusual noise or vibration may point to turbulence, improper sizing, or unsupported piping near the valve.
Likely Causes:
Fixes:
Reducing vibration not only extends valve life but also protects adjacent components from premature wear.
Preventive maintenance is the most effective approach to minimizing valve issues. Here are some general pinch valve troubleshooting best practices:
Inspect regularly: Routine inspection of sleeves, air systems, and fasteners can help catch small problems before they escalate.
Track sleeve life: Keep records of how long each sleeve lasts in specific applications to anticipate when replacements are due.
Choose the right valve type and material: Work with experienced pinch valve manufacturers to select the right valve configuration for your operating conditions.
Train personnel: Ensure operators understand how pinch valves function and how to recognize early signs of trouble.
Pinch valves are robust and simple, but even they require occasional attention to stay in top shape.
From sleeving issues to actuation problems, being proactive with pinch valve troubleshooting ensures reliable performance and minimizes unplanned downtime.
With the right maintenance routine and component selection, pinch valves can serve as low-maintenance flow control solutions even in the harshest environments.
Ресурсы:
Typical Pinch Valve Failures – How to resolve these problems
Troubleshooting Tips for Pinch Control Valve

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
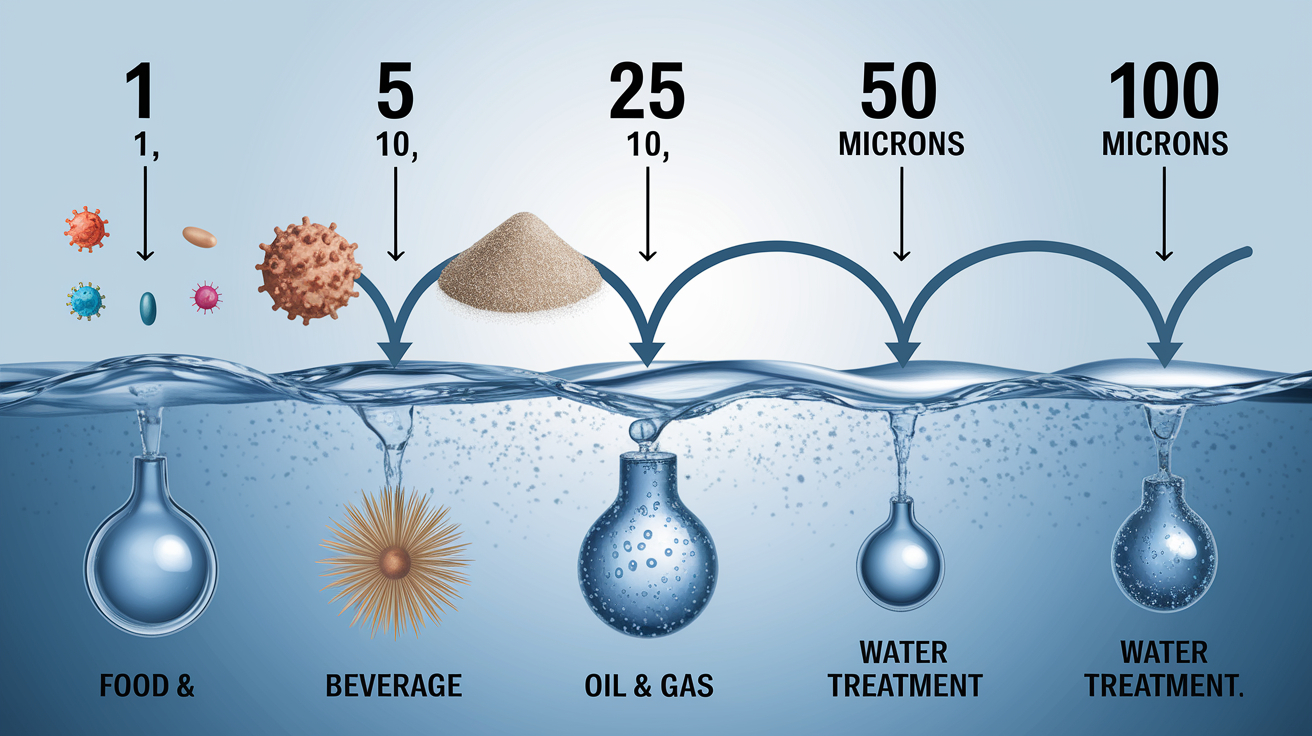
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
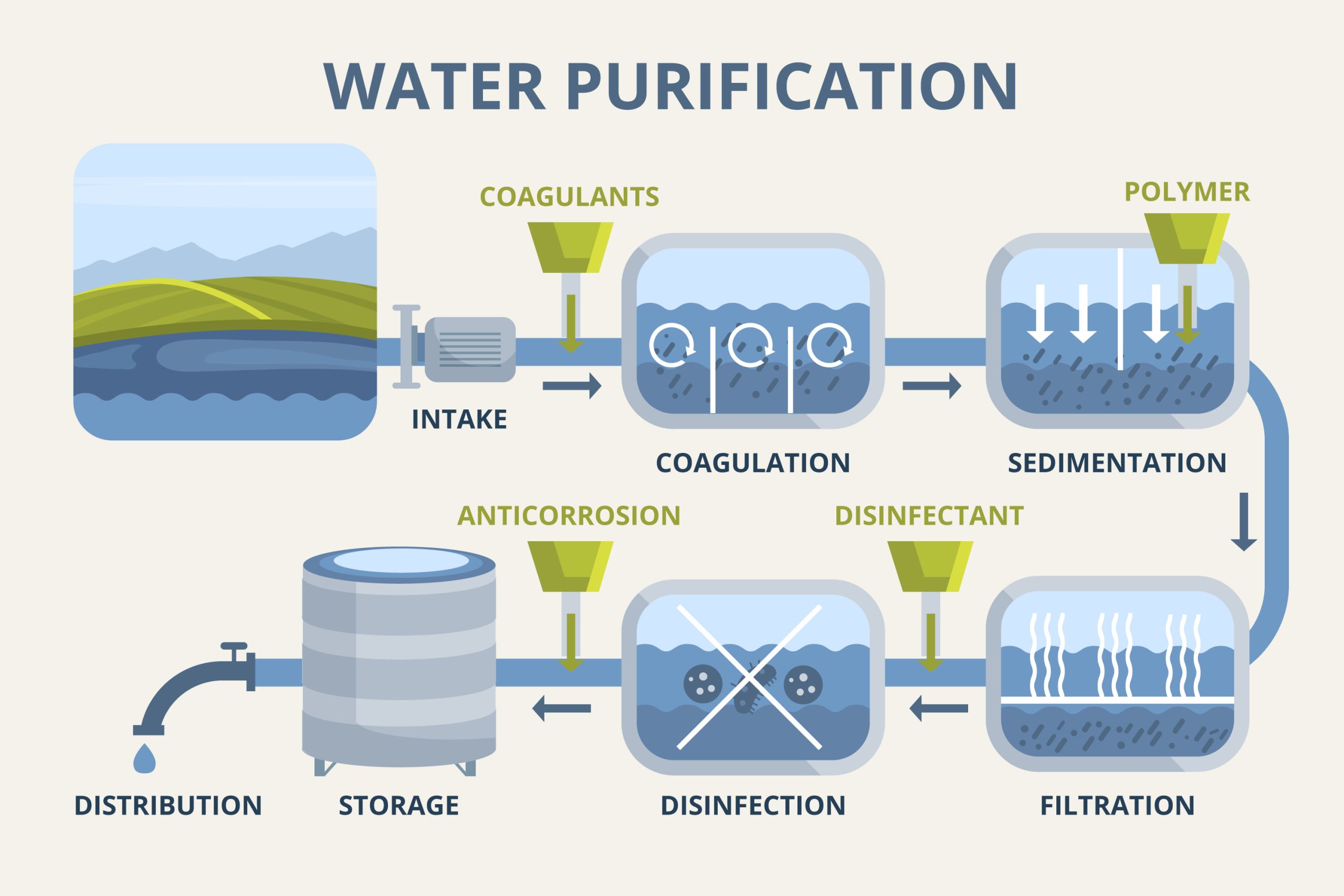
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



