

А мембранный клапан is a type of valve that uses a flexible diaphragm to control the flow of fluids. This valve is part of the linear motion family, which means the moving parts go in a straight line—not in circles like ball или дроссельные клапаны. The elastomeric diaphragm in diaphragm valve is usually made of rubber or plastic and presses against a valve seat inside the diaphragm valve bodies to form a tight seal.
You can use diaphragm valves to control:
The fluid in a diaphragm valve system does not come into contact with the moving parts, such as the stem or actuator. This design ensures that the diaphragm valve remains clean and reduces the risk of damage.
Some diaphragm valves seal against a raised weir (a bump inside the valve), while others use a flat seat. Both designs help regulate or stop flow, depending on your needs.
DO YOU KNOW?
Using a flexible barrier to control fluid flow dates back to ancient times. Early civilizations used basic flexible barriers to manage water in irrigation systems and aqueducts.
These early diaphragm valves were made from natural materials like leather or animal skins. They created a seal against a seat, controlling water flow like modern diaphragm valves. Over time, the principle of using a flexible diaphragm to regulate flow has evolved.

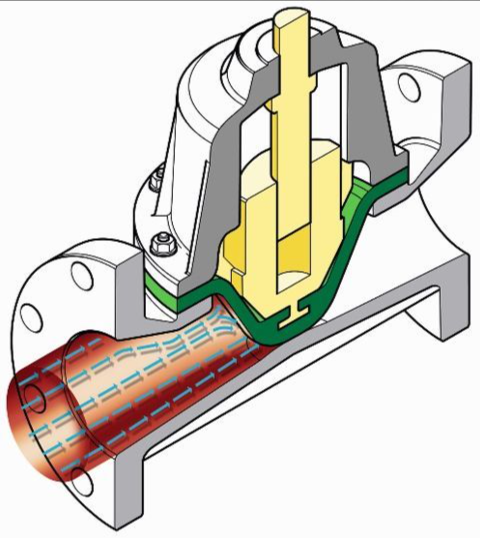
А мембранный клапан works by moving a flexible membrane—called a diaphragm—up and down to control the flow of fluid (Diaphragm valves also called a membrane valve). This motion is linear, meaning it moves in a straight line rather than in circles like some other valves.
Here’s how it operates:
This movement can be powered by an actuator—a device that applies force. Actuators can be:
The diaphragm returns to its closed position either by its own flexibility or with the help of a spring inside the actuator.
In some designs, like weir diaphragm valves, the diaphragm presses against a raised surface (the weir). This lets you control the flow more precisely, which is helpful in low-flow or throttling applications.

А мембранный клапан has several key parts that work together to control fluid flow. Each piece plays a specific role in how the valve operates and how well it performs in different conditions.
Here are the main valve components:
Each part must be compatible with the fluid and environment to ensure the valve works safely and lasts longer.
Diaphragm valves come in different types based on how they seal. The two main types are:
Weir diaphragm valve has a raised barrier inside, called a weir. The diaphragm close and presses down on the weir to stop or control flow.
Straight Through Diaphragm Valves utilize a flat seat to ensure minimal obstruction. The diaphragm seals directly on the flat surface.
Other types include:
Diaphragm valves offer several practical benefits that make them useful in many industries. Their design helps solve common problems with fluid control.
1. Clean and Safe valve Operation
The diaphragm separates the fluid from the moving parts inside the valve. This stops the fluid from touching parts like the stem or actuator, which helps avoid contamination—especially important in food, pharmaceutical, и clean water systems.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Diaphragm valves can handle corrosive chemicals like acids and alkalis. This is because both the valve body and diaphragm can be made from special metals, plastics, или linings that resist chemical damage.
3. Leak-Proof Sealing
The flexible diaphragm forms a tight seal when it presses against the valve seat. This creates bubble-tight shutoff, even under high pressure or vacuum. It’s useful when working with hazardous or expensive fluids.
4. Handling semi Solid media and Slurries Well
These valves can deal with abrasive fluids и slurries (fluid with solid particles). The diaphragm bends around solids to help seal. Some designs also prevent clogging with a straight flow path.
5. Low Maintenance
Есть fewer moving parts, so there’s less wear. The diaphragm is simple to replace without removing the whole valve from the pipe. Also, there’s no need for stem packing, which reduces leaks.
6. Good Flow Control
Weir valves offer more precise flow control, which is helpful in throttling (adjusting fluid flow rate). The linear motion of the diaphragm gives you direct control over how much fluid passes through.
While мембранные клапаны offer many benefits, there are also some limitations you need to consider before choosing them for your system.
1. Pressure Limits
Standard diaphragm valves are best for moderate pressure systems—usually up to 300 psi (about 20 bar). For high-pressure applications, valves like ball или задвижки may be ideally suited.
2. Temperature Restrictions
The diaphragm material limits how hot (or cold) the valve can safely operate. Most diaphragms better to work in moderate pipeline temperatures: от -40°F до 450°F (-40°C to 232°C). If your process involves higher temperatures, it could make diaphragm fails or weaken over time.
3. Diaphragm Wear
Since the diaphragm moves and touches the fluid directly, it can wear out, especially in systems with abrasive particles или frequent cycling. Straight-through types tend to wear faster because they require more flexing.
4. Limited Valve Sizes
Most diaphragm valves are available in sizes from ½ inch to 12 inches (DN 15–300). If your system needs larger valves, you may need to explore other types like butterfly или задвижки.
5. Drainage Issues
In weir-type valves, the raised weir can trap fluid, making full drainage difficult. This can be a problem in batch processes or when switching between fluids.
6. Slower Manual Operation
Manual diaphragm valves often need multiple turns to open or close fully. This makes them slower than quick-action valves like ball или дроссельные клапаны. For fast shut-off, consider automated мембранные клапаны
Choosin’ the right diaphragm valve is mighty important. You need to think about a lot of things to make sure it works right and lasts long. Let’s break it down:
What do you need the valve to do? Think about what you’re controllin’ and how it fits into the whole system.
Fluid Control: How much liquid or gas do you need to control? What’s its speed? Is it thick? This helps pick a valve that can handle the fluid flow.
Industry Matters: Different industries have different rules. Food and medicine need CLEAN valves. Chemical plants need valves that resist BAD stuff.
Types of Bodies: There are different shapes, like straight, angled, and T-shaped. Each one works best for different jobs.
Материал: The valve body needs to handle the fluid. Stainless steel, plastics, and special alloys are common. If the fluid is corrosive, pick other materials that RESISTS it.
Parts: Know the parts! Valve Body, bonnet, diaphragm, valve stem, actuator. Each part matters for how the valve works.
EPDM vs. PTFE: EPDM rubber is good for water. PTFE (Teflon) handles STRONG chemicals. Pick the right one!
What’s the fluid? Make sure the diaphragm can handle the fluid. Otherwise, it’ll break down fast!
Temperature and Pressure ratings: Hot and high-pressure can mess with the diaphragm. Pick a material that can take the heat and pressure.
Types: Manual (hand), electric, air-powered (pneumatic), hydraulic. Pick one that fits your needs.
Давление воздуха: If you use air, make sure the pressure is right. Too low, and the valve won’t work. Too high, and it can break!
Special Features: Some actuators have extra features for better control.
Quality Matters: Selecting high-grade materials ensures durability, reducing wear and tear, and enhancing valve performance over time.
Easy to Fix: Opt for valves with simple disassembly and repair processes, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Whether you’re dealing with corrosive fluids, slurries, or hygienic processes, diaphragm valves offer precise flow control and low maintenance.
For those seeking durability and performance, rubber-lined diaphragm valves from Lianke are a smart choice. With decades of experience and a strong product range, Lianke delivers solutions built to last. If you’re ready to upgrade or start a project, explore Lianke’s diaphragm valves и contact us today to find the right valve for your application.

Мембранные клапаны: типы, применение, особенности и преимущества
Принцип работы мембранного клапана

Choosing the right basket strainer for your system comes down to understanding filtration size, strainer mesh, and how these elements fit into your specific piping setup. Whether you’re working in chemical processing, food production, water treatment, or HVAC, the right strainer ensures system protection, flow efficiency, and long-term equipment performance. This article will help you […]

Installing, operating, and maintaining a basket strainer properly ensures optimal system performance, protects downstream equipment, and extends the life of your filtration system. Whether used in chemical processing, HVAC, food production, or water treatment systems, basket strainers are essential components for removing solid particles from fluids. In this article, we’ll break down the complete lifecycle […]

Valve testing ensures that industrial valves meet strict performance, safety, and durability standards before they are installed in real-world systems. This process verifies that valves operate reliably under pressure, prevent leaks, and perform in extreme conditions such as high temperature or cryogenic environments. Whether it’s a valve leak test or a gas valve test, the […]

The most effective way to resolve pinch valve issues is to identify the root cause early—whether it’s sleeve wear, actuation failure, or leaks—and apply targeted troubleshooting steps to restore performance. Pinch valves are favored for their durability and simplicity in handling slurries, abrasive materials, and corrosive fluids. But like any component, they can develop problems […]



