

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient.
If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing the wrong class can lead to pressure failures or safety hazards. In this article, we’ll break down what ANSI Class Ratings really mean, how they’re calculated, and how to choose the right one for your Y strainer flange.
ANSI stands for the American National Standards Institute. It’s a nonprofit organization that sets the standards for products, systems, and services in the U.S. These standards are designed to ensure safety, consistency, and compatibility across industries.
ANSI works alongside ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) on flanges. The specific standards for flange ratings are found in ASME B16.5, which outlines dimensions, materials, and pressure-temperature ratings for pipe flanges and flanged fittings.
An ANSI Class Rating is a pressure-temperature classification for a flange. It defines the maximum pressure the flange can handle at specific temperatures.
There are seven standard ANSI classes used for flanges:
You might also see these listed as lbs., pressure rating, or #—all of which refer to the same concept.
Y strainers are key components in pipeline systems. They catch debris and protect valves, pumps, and other equipment. But it can fail if the flange on a Y strainer isn’t strong enough for the system’s pressure or heat.
That’s where ANSI class ratings come in. You ensure the flange won’t leak or burst by matching the class rating to your system’s pressure and temperature.
The ANSI rating of a flange doesn’t just depend on pressure—it also depends on temperature and material.
For example, a Class 300 carbon steel flange may handle up to 605 PSI at 500°F. At 700°F, that same flange drops to 530 PSI.
This change happens because materials expand and weaken at higher temperatures. Every ANSI class is tied to a temperature-pressure chart, which helps engineers choose the right thickness and strength based on actual operating conditions.
One common misconception is that a Class 300 flange = 300 PSI. That’s not true.
PSI (pounds per square inch) is a unit of pressure. ANSI classes, on the other hand, are broader categories that factor in PSI plus:
So, while PSI is part of the formula, it’s not the whole story. For example, a Class 300 flange made of carbon steel might withstand 600+ PSI at lower temps, but the same class in cast iron would have a lower PSI limit.
Always check the material-specific pressure-temperature chart before making a decision.
Before selecting a Y strainer flange, gather these three critical details:
Then:
If you’re unsure where to find the right chart, resources like The Engineering Toolbox offer reliable tables based on ASME data.
Example 1: You’re installing a stainless-steel Y strainer in a system running at 450°F and 500 PSI. Based on ASME B16.5, a Class 600 flange is appropriate.
Example 2: Your pipeline is low-pressure—around 150 PSI—and the fluid temp doesn’t exceed 200°F. In this case, a Class 150 flange made of ductile iron might be enough, but it depends on chemical compatibility and safety margins.
Using the wrong flange class can result in costly failures, leaks, or even safety hazards. It’s not just about meeting minimum pressure requirements—it’s about matching the flange to both the temperature and pressure over time.
Taking the time to understand ANSI flange ratings for Y strainers ensures long-term performance and system reliability.
Now that you understand ANSI Class Ratings for Y Strainer Flanges, you’re in a much better position to make informed decisions. Always check your system’s pressure and temperature specs and cross-reference them with the proper ASME charts before selecting a flange class.
At Клапан Lianke, we offer a full line of Y strainers with ANSI-rated flanges that meet global quality standards. Whether you’re building a new system or upgrading components, we make it easy to find the right fit.
👉 Explore our Y Strainers here


ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
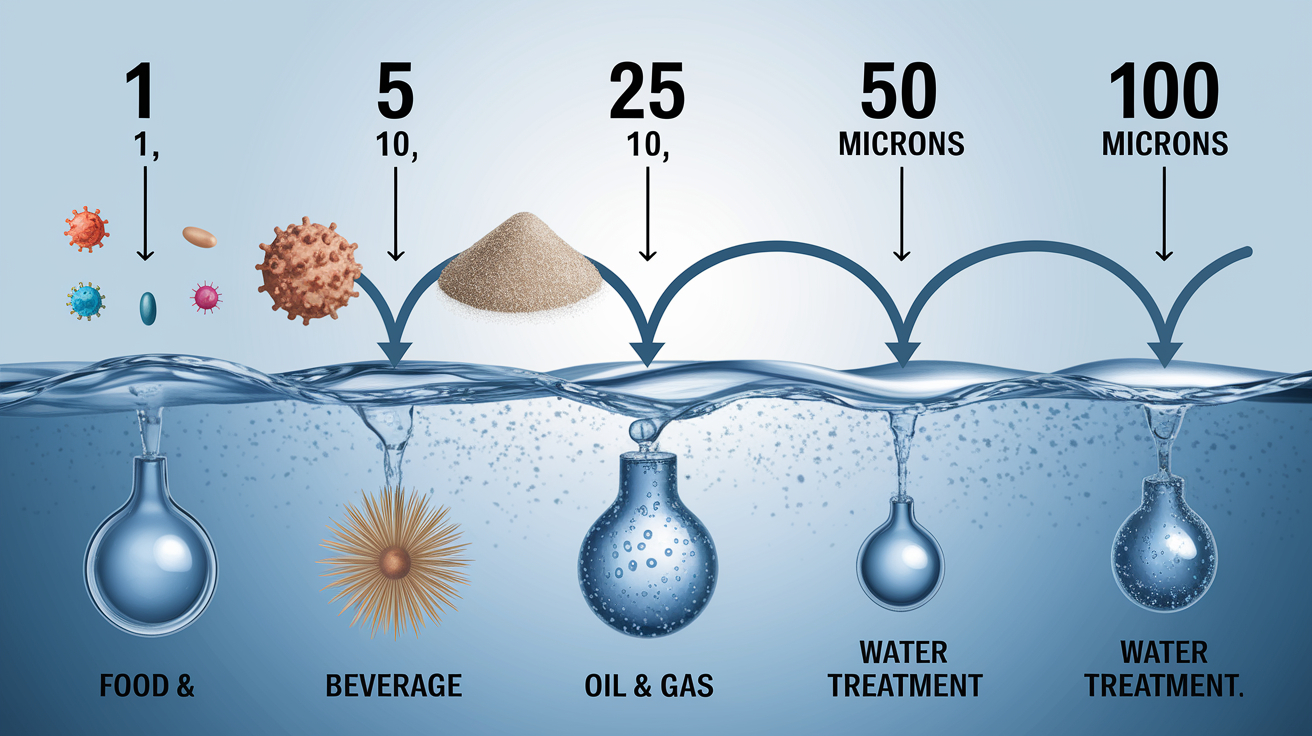
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
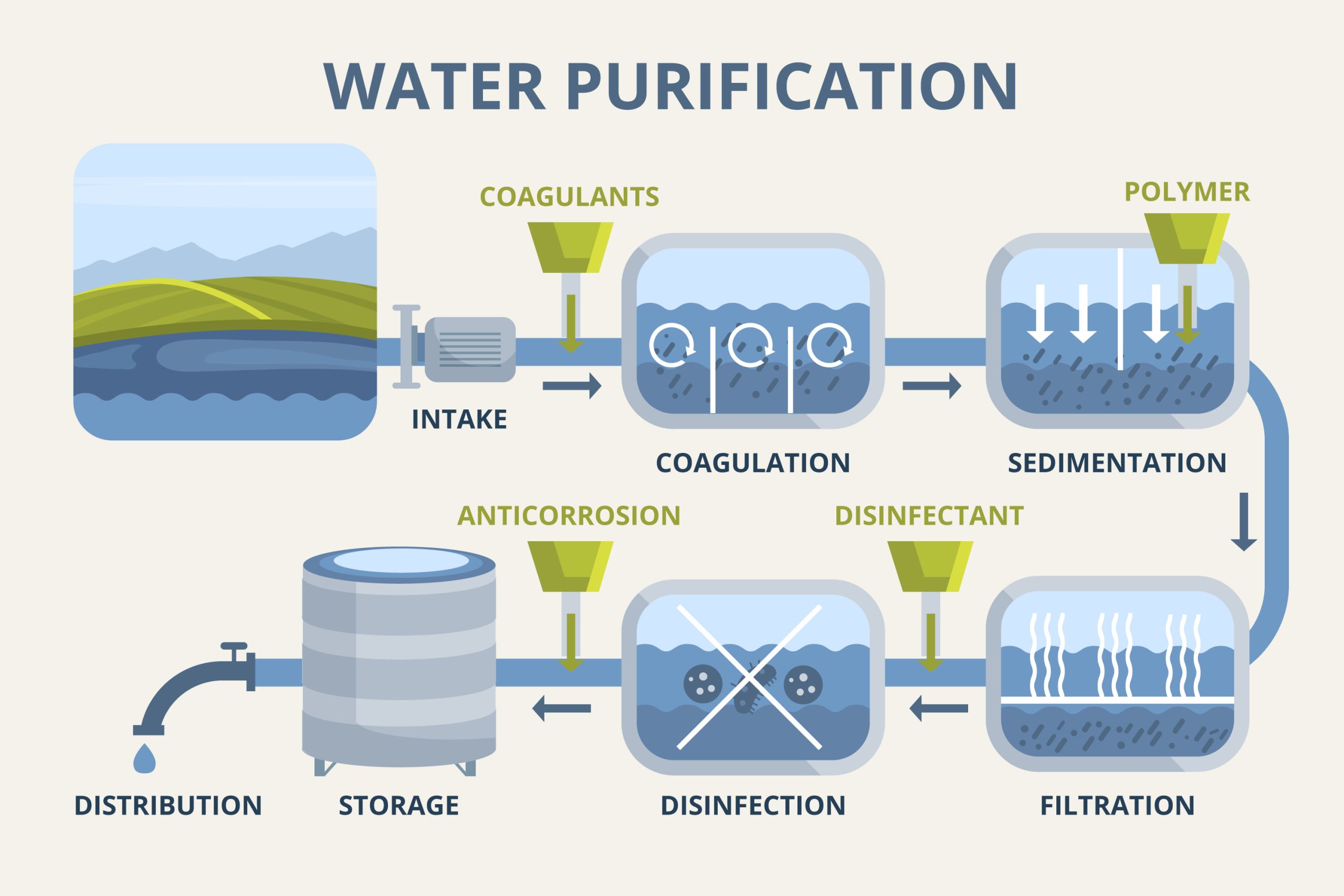
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



