

Choosing the right coador de cesta for your system comes down to understanding filtration size, strainer mesh, and how these elements fit into your specific piping setup.
Whether you’re working in chemical processing, food production, water treatment, or HVAC, the right strainer ensures system protection, flow efficiency, and long-term equipment performance.
This article will help you navigate critical aspects of filtration, including how to evaluate strainer mesh sizes, explore mesh upgrades for strainers, and understand the role of a strainer in piping.
We’ll also outline what you should consider when selecting the ideal basket strainer for your application.
A basket strainer is a device installed in a pipeline to remove debris and particles from the flow of liquid.
It helps shield critical downstream components—like pumps, valves, and nozzles—from debris-related damage.
It typically consists of a perforated or mesh-lined basket housed inside a metal body, allowing fluid to pass through while catching solids.
In many industrial systems, the basket strainer is the first line of defense in maintaining fluid cleanliness and operational efficiency.
Filtration is more than just removing visible debris—it’s about protecting precision components from clogging or abrasion.
Particles even smaller than the eye can see can cause system inefficiencies, reduced flow rates, or long-term equipment degradation.
This is where selecting the right filtration size and strainer mesh comes into play.
Filtration size indicates the minimum particle size a strainer can trap as fluid passes through. It’s typically measured in microns.
One micron is one-millionth of a meter, and smaller micron ratings indicate finer filtration.
Strainer mesh sizes, on the other hand, relate to how many openings (or threads) exist per linear inch in the mesh.
The higher the mesh number, the finer the mesh, and the smaller the particles it can filter out.
For example:
| Mesh Size | Opening Size (Approx.) | Micron Equivalent |
| 20 mesh | 840 microns | Filtração grosseira |
| 60 mesh | 250 microns | Medium filtration |
| 100 mesh | 150 microns | Fine filtration |
| 200 mesh | 74 microns | Extra-fine |
The strainer mesh material significantly affects performance and longevity.
Stainless steel is commonly used for its resistance to corrosion and wear, especially in chemical or high-pressure environments.
However, other alloys or coatings may be used depending on the media being filtered.
For example, in highly corrosive applications, Hastelloy or Teflon-coated baskets may be used.
In food-grade environments, electropolished stainless steel offers both corrosion resistance and sanitary compliance.
Mesh upgrades for strainers are essential when you need more precise filtration or encounter frequent clogging.
Upgrading to a finer mesh can improve fluid cleanliness but may also reduce the flow rate if the surface area isn’t increased.
Situations that often call for a mesh upgrade include:
When upgrading, ensure the housing can accommodate the higher resistance caused by finer mesh.
Consulting your system’s flow and pressure specs before selecting finer filtration is critical.
The strainer in piping serves a preventive function—removing foreign particles from fluids to avoid equipment failure or contamination.
Typically installed upstream of critical components like control valves, heat exchangers, or pumps, it plays a vital role in:
Proper placement in the pipeline is key.
Basket strainers should be accessible for easy maintenance and located in areas where fluid velocity supports debris collection without causing turbulence.
Two of the most common types of basket strainers include:
Simplex basket strainers have one filtration chamber, requiring system shutdown when it’s time to clean. It’s ideal for applications where shutdowns are acceptable or infrequent.
A duplex basket strainer consists of two baskets in parallel with a diverter valve, allowing continuous operation during maintenance.
It’s best for critical systems that must remain online without interruption.
Proper installation is vital to the strainer’s effectiveness. Key considerations include:
While selecting the right basket strainer is essential, regular maintenance keeps it operating effectively. Here’s how to clean a strainer:
Inspection frequency depends on system conditions, but a general rule is to clean the basket at least once a month or more often in high-debris environments.
When selecting a strainer, match the following to your system requirements:
If your system experiences varying process demands, consider basket strainers with interchangeable mesh elements or modular housings that allow future upgrades.
Choosing the right basket strainer goes beyond just size—it’s about understanding how strainer mesh, mesh upgrades for strainers, and filtration size fit into your system’s operational demands.
From selecting the appropriate strainer mesh sizes to installing and maintaining it effectively, each step plays a role in maximizing system performance and equipment longevity.
Remember, the right strainer in piping can save time, prevent damage, and ensure consistent output.
Recursos:
Guide: How to Select and Size Filtration & Strainers
Ultimate Guide to basket strainer
Ultimate Guide for Choosing the Correct Basket Strainer

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
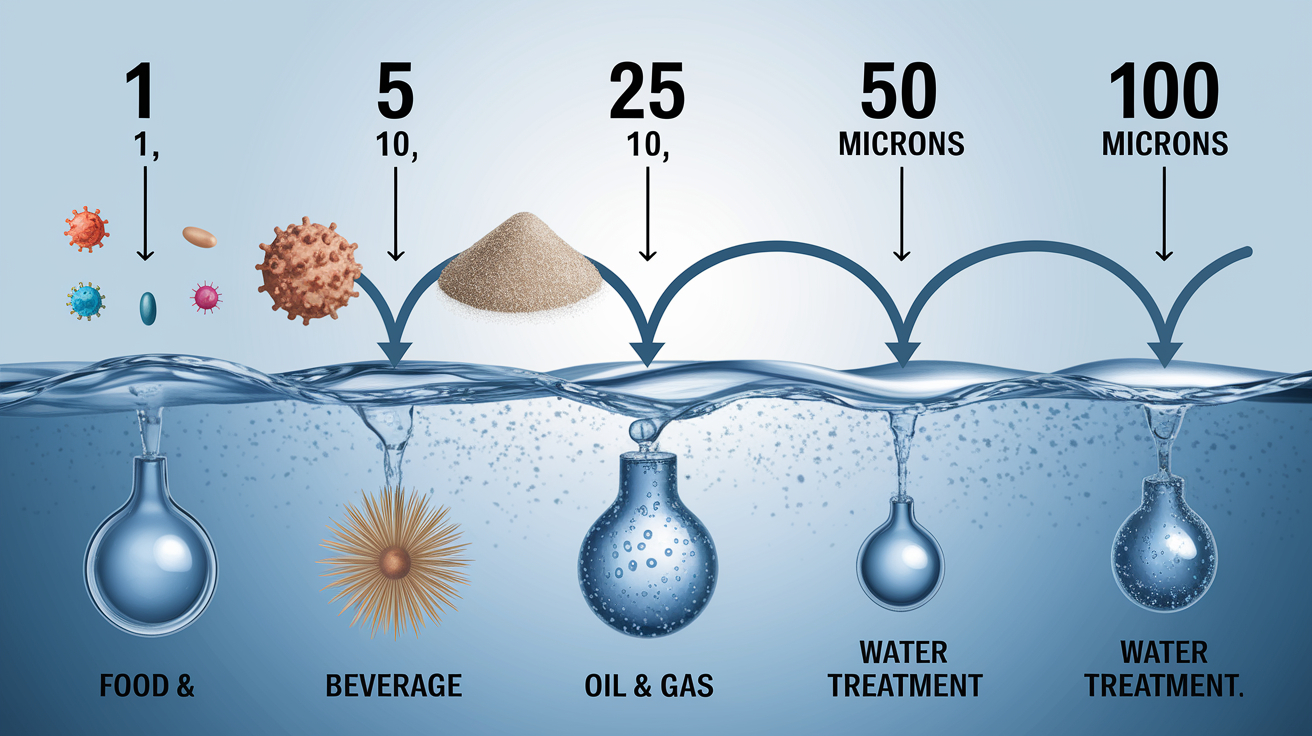
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
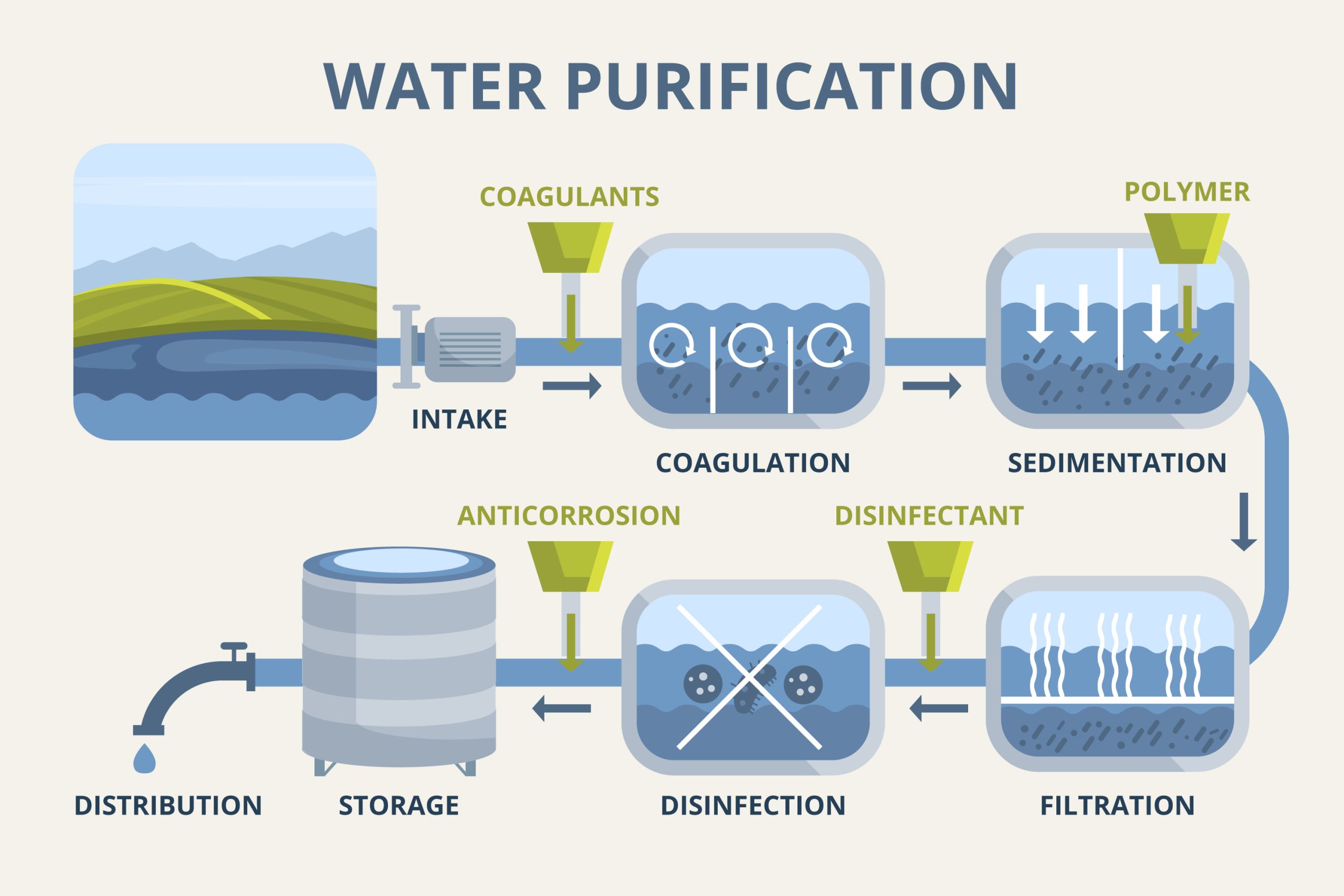
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



