

Plásticos e elastômeros são materiais essenciais em indústrias que vão da fabricação automotiva a dispositivos médicos. Embora ambos sejam polímeros (longas cadeias de moléculas repetidas), suas propriedades e aplicações diferem significativamente. Este guia detalha suas distinções técnicas, apoiadas por pesquisas e dados da indústria, para ajudar você a fazer escolhas informadas de materiais.
Plásticos são polímeros sintéticos feitos de monômeros como etileno ou propileno. Eles são categorizados em dois tipos:
Elastômeros, frequentemente chamados de borrachas, são polímeros com propriedades elásticas. Suas cadeias moleculares são reticuladas, permitindo que se estiquem sobre 100% e retornem à sua forma original. Exemplos comuns incluem silicone e EPDM (Indústrias Osborne).
| Propriedade | Plásticos | Elastômeros |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticidade | Baixo (alongamento ≤ 10%) | Alto (alongamento 100–700%) |
| Resistência ao calor | Varia: PE (80°C), PEEK (250°C) | Moderado: Silicone (230°C), EPDM (150°C) |
| Reciclabilidade | Termoplásticos: Sim; Termofixos: Não | Limitado (estrutura reticulada) |
Os elastômeros absorvem o estresse mecânico por meio de sua estrutura molecular enrolada. Por exemplo, os anéis de vedação de silicone se esticam para selar as lacunas sob pressão, mas retornam à forma quando a carga é removida (Estudo PMC).
Plásticos como policarbonato mantêm a forma sob cargas estáticas, mas podem rachar sob impacto repentino. Tubos de PVC suportam pressão de água constante, mas podem falhar se dobrados repetidamente.
Plásticos na Indústria
Elastômeros em Ação
Plásticos
Elastômeros
Plásticos fornecem integridade estrutural, enquanto elastômeros fornecem flexibilidade. Entender suas diferenças garante a seleção ideal de materiais para durabilidade e desempenho industrial.

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
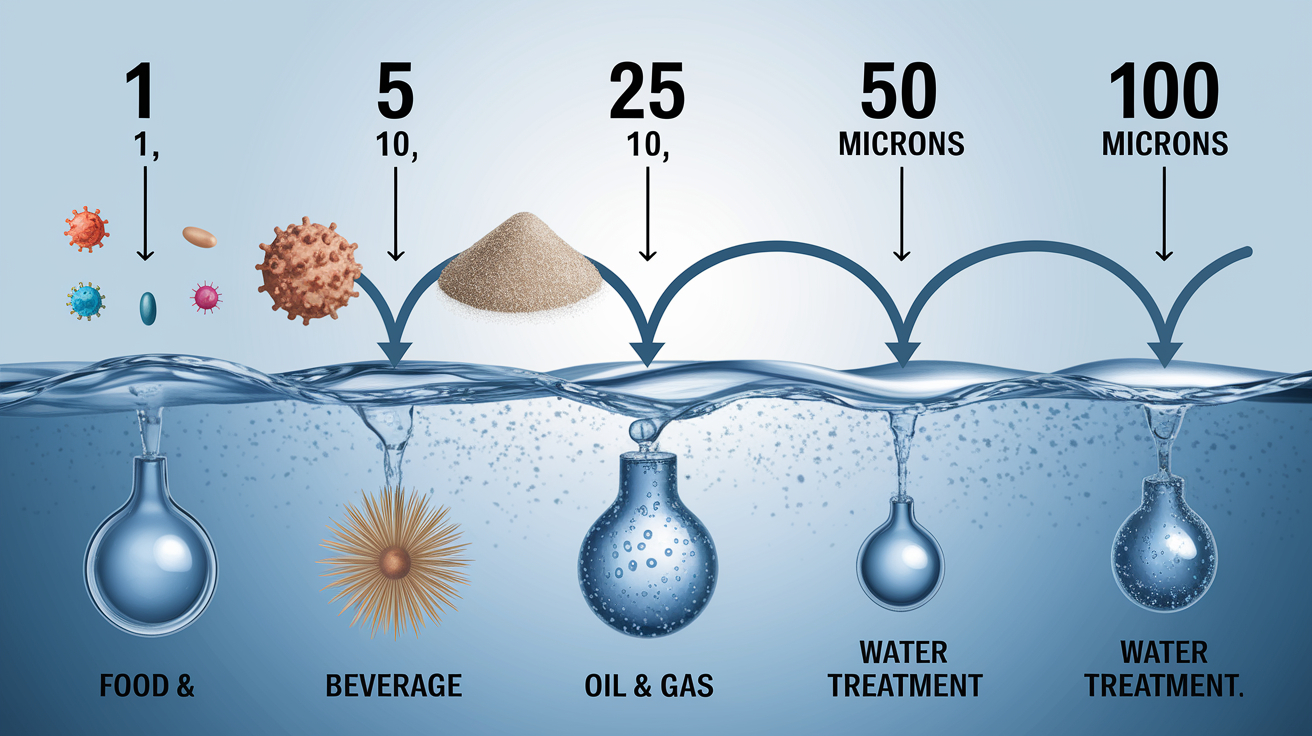
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
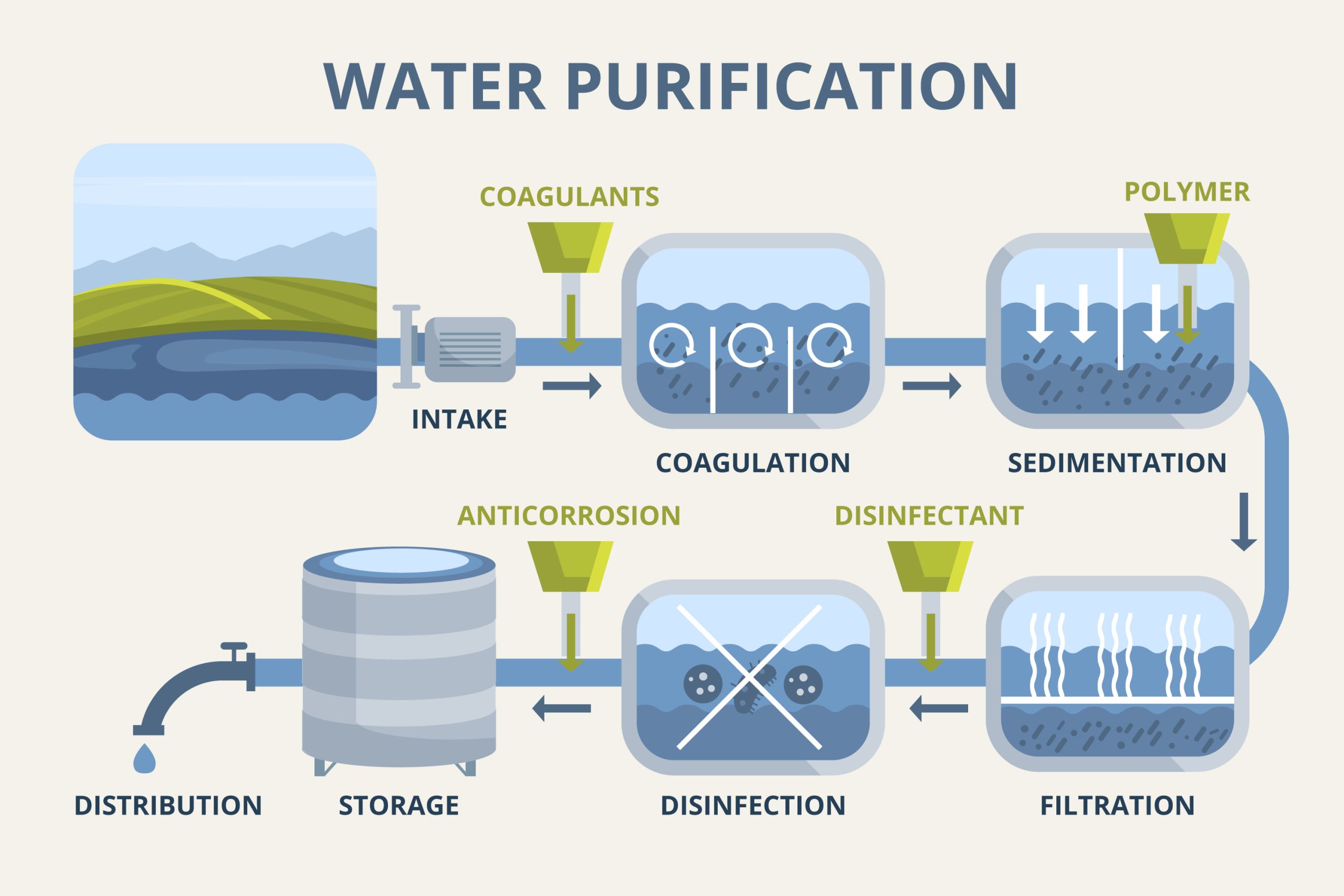
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



