

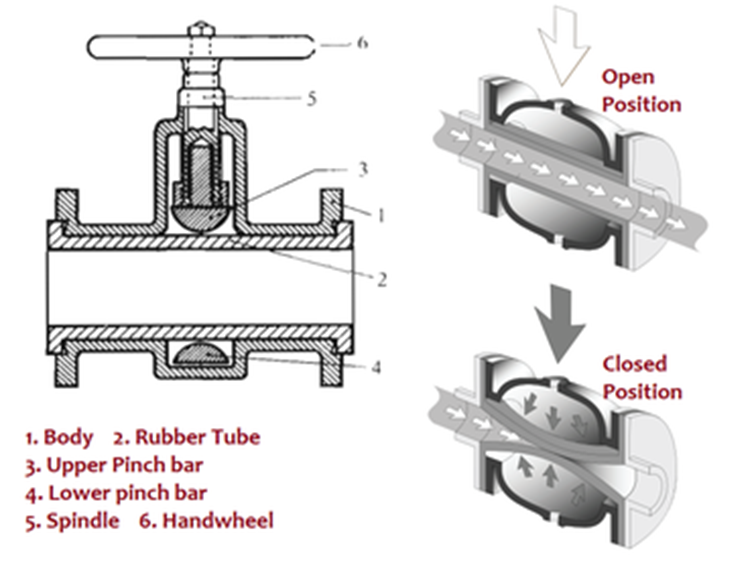
An air pinch valve with flange is a flow-control device that uses compressed air (4–8 bar) to open or close a rubber sleeve, regulating the passage of abrasive, corrosive, or viscous media. The flange connection ensures secure pipeline mounting, complying with standards like DIN EN 1092 or ANSI B16.5. This guide explains its design, materials, and industrial applications without promotional bias.
| Elastomer | Temperature Range | Best For |
| Natural Rubber (NR) | -40°C to +80°C | Abrasive slurries, mining tailings. |
| EPDM | -30°C to +150°C | Steam, acids (pH 3–12). |
| Viton (FKM) | -20°C to +200°C | Oils, solvents, chlorinated chemicals. |
| NBR | -30°C to +100°C | Fuels, oils, non-polar fluids. |
| Standard | Pressure Rating | Common Use Cases |
| DIN EN 1092 (PN10/16) | 10–16 bar | European water treatment, chemical plants. |
| ANSI B16.5 (150#) | 19.6 bar | U.S. oil/gas, high-pressure slurry systems. |
| Feature | Pinch Valve | Gate Valve | Ball Valve |
| Clogging Risk | None (full bore) | High (gate grooves) | Moderate (ball cavity) |
| Maintenance | Replace sleeve only | Stem/packing repairs | Seat/ball replacement |
| Abrasion Resistance | High (sleeve absorbs wear) | Low (metal parts wear) | Moderate |
Q: How long do air pinch valve sleeves last?
A: 1–5 years, depending on abrasion and chemical exposure. Mining slurries wear sleeves faster than water.
Q: Can air pinch valve sleeve handle high temperatures?
A: Yes. EPDM sleeves withstand +150°C; Viton handles +200°C.
Q: What’s the maximum pressure rating for air pinch valve?
A: DN25–DN150: 6 bar; DN200: 4 bar; DN250–DN450: 3 bar.
Q: Can air pinch valve work with viscous fluids?
A: Yes. Full-bore design prevents clogging in adhesives or sludge.
Air pinch valves with flanges offer reliable flow control in harsh environments, with minimal maintenance and no flow obstruction. Selecting the right sleeve material and flange standard ensures longevity in applications from mining to food processing.

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
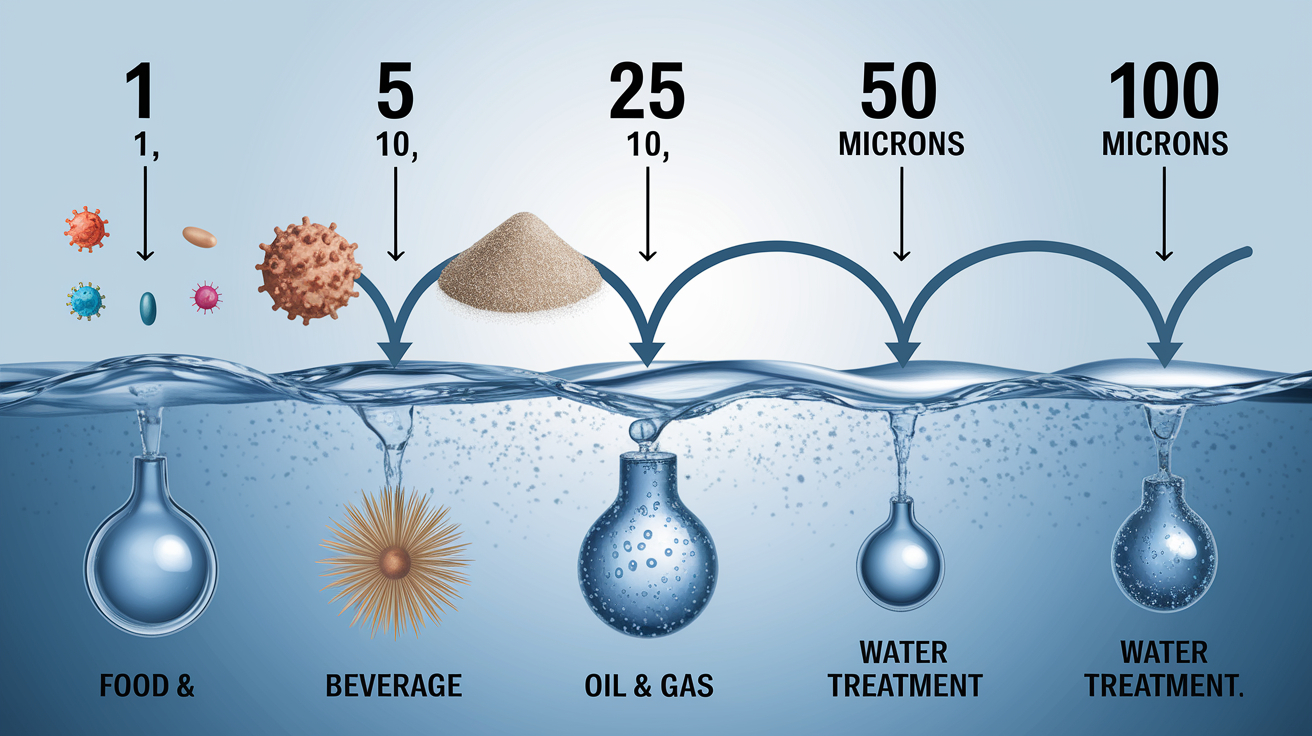
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
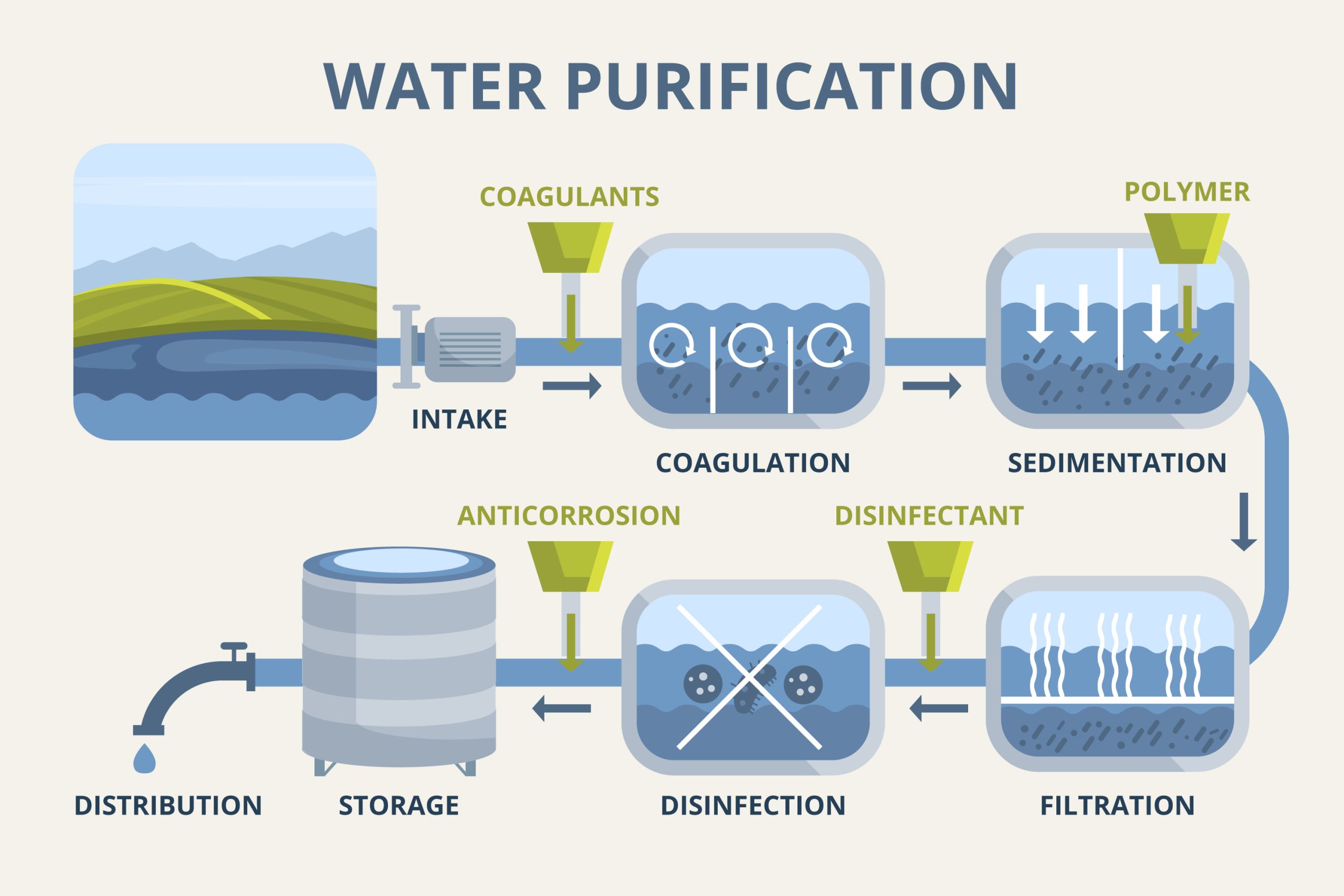
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



