

Pneumatic pinch valves are crucial components in fluid control systems, and their lifespan is influenced by several factors, including pneumatic actuators and controls, sleeves, pressure conditions, temperature extremes, cycle rate, and the cleanliness of media. The pneumatic actuators manipulate the flexible sleeves that control fluid flow; thus, their performance directly affects the valve’s longevity.
For instance, sleeves typically last between 2 to 5 years, depending on the abrasiveness of the media and operating conditions, while pneumatic actuator components can endure around 5 million cycles (approximately 5 years) under optimal conditions.
Ever wondered how long pneumatic pinch valves last and what factors influence their lifespan?
This article covers the working principles, factors affecting lifespan, typical longevity, and signs of wear, and maintenance practices.
Pneumatic pinch valves are used to control the flow of various media in pipelines. Their operation is based on a simple yet effective mechanism that utilizes a flexible elastomeric sleeve which can be pinched to open or close the valve.
Excessive or fluctuating pressure can lead to increased wear on the valve seals and components. High pressures may cause catastrophic failures, such as cracking or breaking parts of the valve, while low pressures may not provide sufficient pinching force, leading to leakage.
Temperature plays a critical role in the lifespan of pinch valves. Extreme heat can degrade seal materials, while low temperatures can cause moisture to freeze, potentially damaging seals and preventing proper operation. Each seal material has specific temperature ratings that must be adhered to for optimal performance.
The frequency of actuation (cycle rate) significantly impacts wear and tear on the valve. High cycle rates can generate heat from friction, leading to premature failure. Conversely, if a valve remains mostly open and only closes when necessary, its internal components may experience less wear, extending their life.
Debris or contaminants in the media can damage seals and other internal components. While some valve designs are more resistant to debris, maintaining clean media is crucial for minimizing wear and prolonging valve life.
The choice of seal material is vital for compatibility with the media being transported and for ensuring durability under operational stresses. Different materials have varying resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and wear. For example, elastomeric materials like EPDM or FKM are often used in internal pinch valves for their superior lifespan compared to standard rubber.
Here’s a table summarizing the typical lifespan of pneumatic valve components under different factors.
| Factors | Components Affected | Typical Lifespan |
| Pressure Conditions | Seals | 1 to 3 years (depending on application) |
| Body and Housing | 10+ years (with proper maintenance) | |
| Actuator Components | 5 million cycles (approx. 5 years) | |
| Temperature Extremes | Coil Encapsulation | Varies, typically several years |
| Internal Components | 5 to 10 years (depending on material) | |
| Cycle Rate | Actuators and Controller | 5 million cycles (approx. 5 years) |
| Bearings and Guides | 3 to 5 years | |
| Cleanliness of Media | Pinch Valve Sleeves | 2 to 5 years (depending on abrasiveness) |
For high-quality pneumatic pinch valves, consider Lianke Valve. We are known for our durable and reliable products, which are designed to handle various industrial applications efficiently.
Our expertise in manufacturing ensures that our valves, including welding pneumatic pinch valves meet stringent performance standards.
In conclusion, understanding the lifespan and maintenance of pneumatic pinch valves is essential for ensuring efficient and reliable operation. By selecting high-quality products like those from Lianke Valve, known for their durability and performance, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your valve systems.
Ready to enhance your operations? Explore Lianke Valve’s range of pneumatic pinch valves today!
Answer: Pneumatic pinch valves are commonly used in industries such as wastewater treatment, mining, food and beverage processing, and chemical handling.
They are ideal for applications involving abrasive or corrosive media due to their robust design and ability to handle a wide range of materials.
Answer: Pneumatic pinch valves generally require less maintenance compared to traditional mechanical valves. This is because they have fewer moving parts and are less prone to wear and tear. The flexible rubber sleeve in pinch valves can be easily replaced, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Answer: While pneumatic pinch valves are typically used in low to medium pressure applications, there are specialized designs available that can handle higher pressures. It is important to select a valve that is rated for the specific pressure requirements of your application to ensure safety and reliability.
Answer: Pneumatic pinch valves offer several environmental benefits, including reduced energy consumption and lower emissions. Since they use compressed air for actuation, they do not require electrical power, making them more energy-efficient.
Additionally, their ability to handle abrasive and corrosive media without leaking helps prevent environmental contamination.
How to Extend the Cycle Life of Your Valve
The life expectancy of a pinch valve sleeve
Fixing Common Pneumatic Control Valve Problems
Discover the Secrets to Troubleshooting Pinch Valves Issues
Valve Maintenance Guide: Preventive Measures and Scheduling Best Practices
Valve Maintenance and Life Expectancy Tips
The Leading Manufacturer of Pinch Valves, Fluorine Lined Valves, and Filters

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
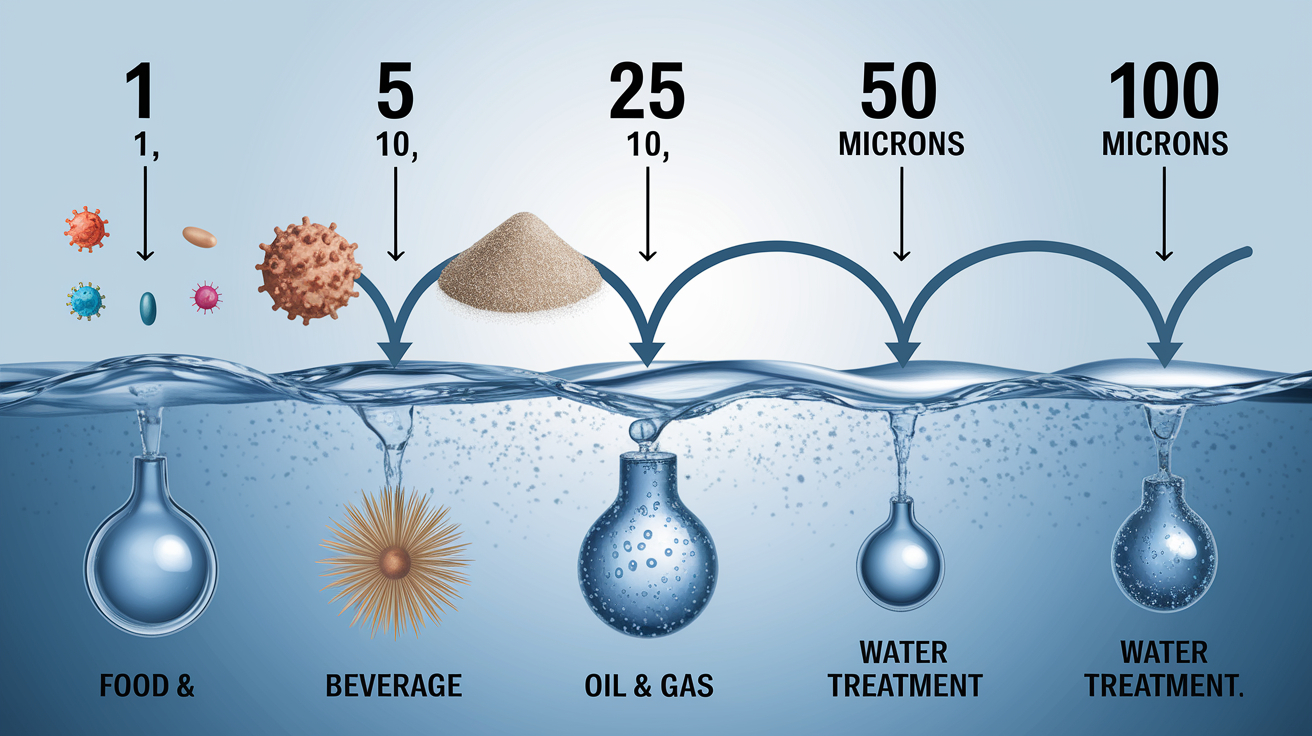
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
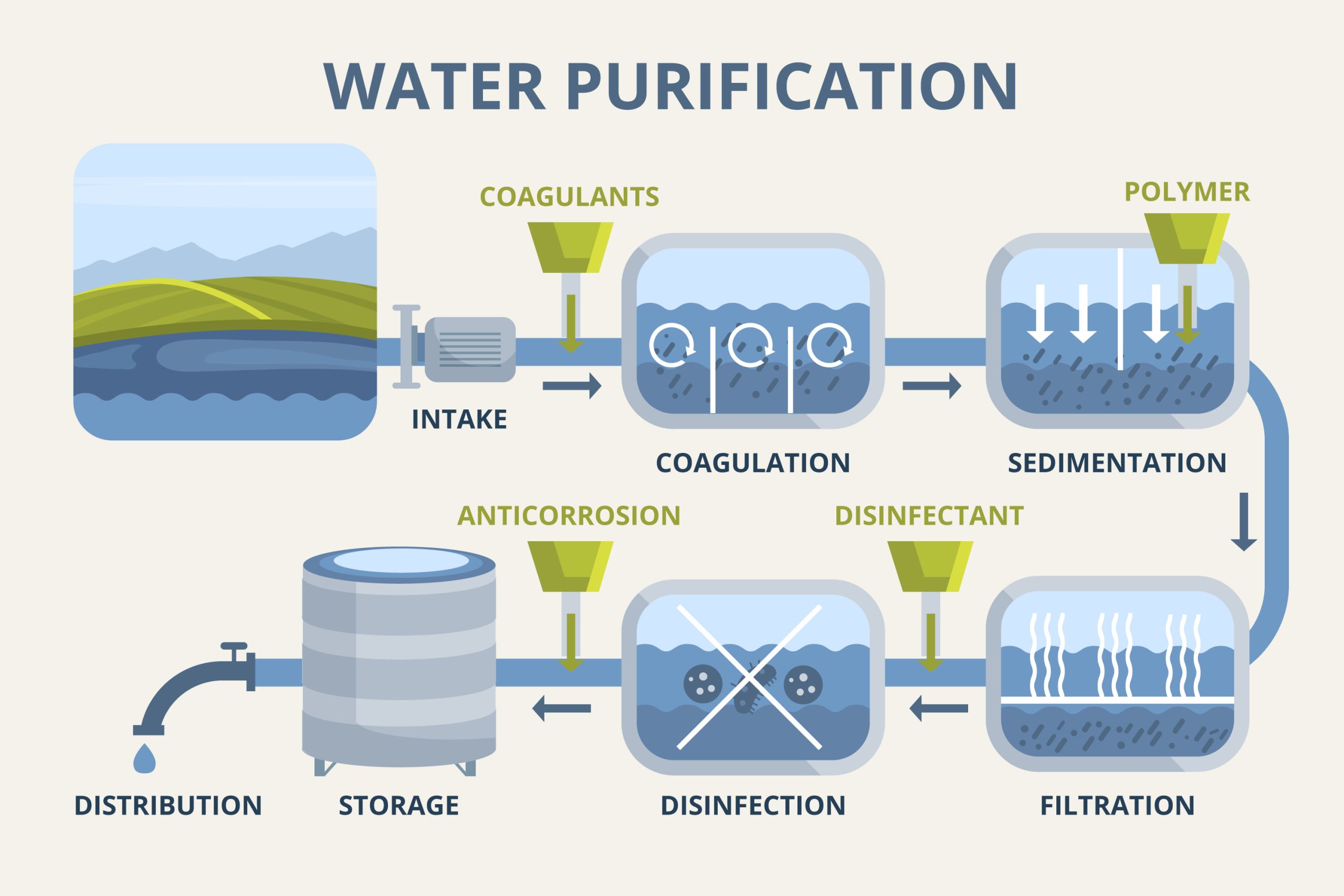
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



