

Lined ball valves feature a protective lining that offers superior corrosion resistance and can handle a wider range of temperatures, making them ideal for aggressive chemical applications.
In contrast, unlined ball valves are typically made from metal and may require additional coatings for protection, leading to more frequent maintenance and a shorter lifespan in harsh environments. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the application.
Which valve is best suited for your application? Let’s find out!
A lined ball valve is a type of valve that features a ball with a hole through the middle, allowing fluid to pass through when aligned with the pipe.
The interior surfaces of these valves are lined with materials like PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) or Teflon, which provide excellent chemical resistance and durability.
| Material | Chemical Resistance | Temperature Range | Mechanical Strength | Electrical Insulation | Permeation Rate (g/m²/day) |
| PTFE | Excellent | -200°C to 260°C | Low | Excellent | 0.1 – 0.4 |
| PFA | Excellent | -200°C to 260°C | Medium | Excellent | .05 – 0.3 |
| FEP | Excellent | -200°C to 205°C | Medium | Excellent | 0.1 – 0.25 |
| PVDF | Good | -40°C to 150°C | High | Good | 0.5 – 1.5 |
| ETFE | Good | -200°C to 270°C | High | Excellent | 0.2 – 0.6 |
| Materials | Resistant Chemicals |
| PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | Acetic Acid (glacial)AcetoneHydrochloric AcidNitric AcidSulfuric AcidHydrogen PeroxideAmmonium Hydroxide |
| PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) | Acetic Acid (glacial)Hydrochloric AcidNitric AcidSulfuric AcidHydrogen Peroxide |
| FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) | Acetic Acid (glacial)Hydrochloric AcidNitric AcidSulfuric Acid |
| PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) | Acetic Acid (up to 40%)Hydrochloric Acid (diluted)Nitric Acid (up to 20%) |
| ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene) | Acetic Acid (up to 30%)Hydrochloric Acid (diluted) |
| Materials | Compatible Chemicals |
| PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | AcetaldehydeAcetamideBenzeneChloroformCitric AcidDiethyl Ether |
| PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) | AcetaldehydeAcetamideBenzeneChloroformFormic Acid |
| FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) | AcetaldehydeBenzeneChloroform |
| PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) | Ammonium HydroxideSodium Hydroxide (diluted) |
| ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene) | Sodium Hydroxide (diluted) |
An unlined ball valve is a type of valve that does not have an internal lining to protect against corrosion or chemical attack.
These valves are typically made from materials like stainless steel, brass, or PVC, and are used in applications where the fluid being handled is not corrosive or chemically aggressive.
Unlined ball valves are typically made from materials that can withstand the specific conditions of the application without the need for additional lining. Here are some common materials used:
| Aspect | Benefits | Limitations |
| Cost-Effective | Less expensive than lined valves like PTFE lined ball valves | Not suitable for handling corrosive or aggressive chemicals |
| Durability | Made from robust materials like stainless steel or brass | Materials can corrode over time in certain environments |
| Ease of Operation | Simple to operate, providing quick and reliable shut-off | Not recommended for throttling applications |
| Low Maintenance | Requires less maintenance compared to lined valves | Higher risk of leakage without additional sealing provided by a lining |
| Versatility | Suitable for a wide range of applications, including water, oil, and gas | Lacks the chemical resistance and durability of lined valves |
| Aspect | Lined Ball Valves | Unlined Ball Valves |
| Corrosion and Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance due to PTFE or Teflon lining, ideal for handling corrosive chemicals | Limited resistance, suitable for non-corrosive fluids like water, oil, and gas |
| Pressure and Temperature Suitability | Suitable for a wide range of pressures and temperatures, typically up to 160°C (320°F) and 250 psi | Suitable for moderate pressures and temperatures, depending on material (e.g., stainless steel up to 200°C (392°F) and 16 bar (232 psi) |
| Materials and Construction | Lined with materials like PTFE or PFA; body often made of stainless steel or ductile iron | Made from materials like stainless steel, brass, or PVC |
| Industries Used | Chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, pulp and paper, semiconductor, mining | Residential, commercial plumbing, oil and gas, general manufacturing |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance needs due to corrosion resistance; longer lifespan in harsh environments | Higher maintenance needs; potential for corrosion and wear in certain environments |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Generally more expensive due to the lining materials and manufacturing process | More cost-effective for general-purpose applications |
Choosing between lined and unlined ball valves depends on your specific application needs, especially regarding chemical resistance and cost.
Lianke Valve offers high-quality fluorine lined ball valves that provide excellent durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for demanding industrial environments.
Ready to enhance your system’s performance? Contact Lianke Valve today to find the perfect solution for your needs!
Answer: Yes, lined ball valves, especially those lined with materials like PFA, can handle higher temperatures compared to unlined ball valves. PFA-lined valves can typically withstand temperatures up to 260°C (500°F), making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Answer: Unlined ball valves are commonly used in industries such as HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), water treatment, and food and beverage processing. These industries often handle non-corrosive fluids, making unlined ball valves a cost-effective choice.
Answer: The installation process for both lined and unlined ball valves is generally similar, involving proper alignment and securing of the valve in the pipeline. However, extra care must be taken with lined ball valves to avoid damaging the lining during installation, which could compromise their chemical resistance.
Different Types of Fluorine Lined Valves and Their Applications
What Are PFA Lined Ball Valves?
Chemical Resistance Guide of PTFE & Filled PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and Teflon® Chemical Compatibility Chart

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
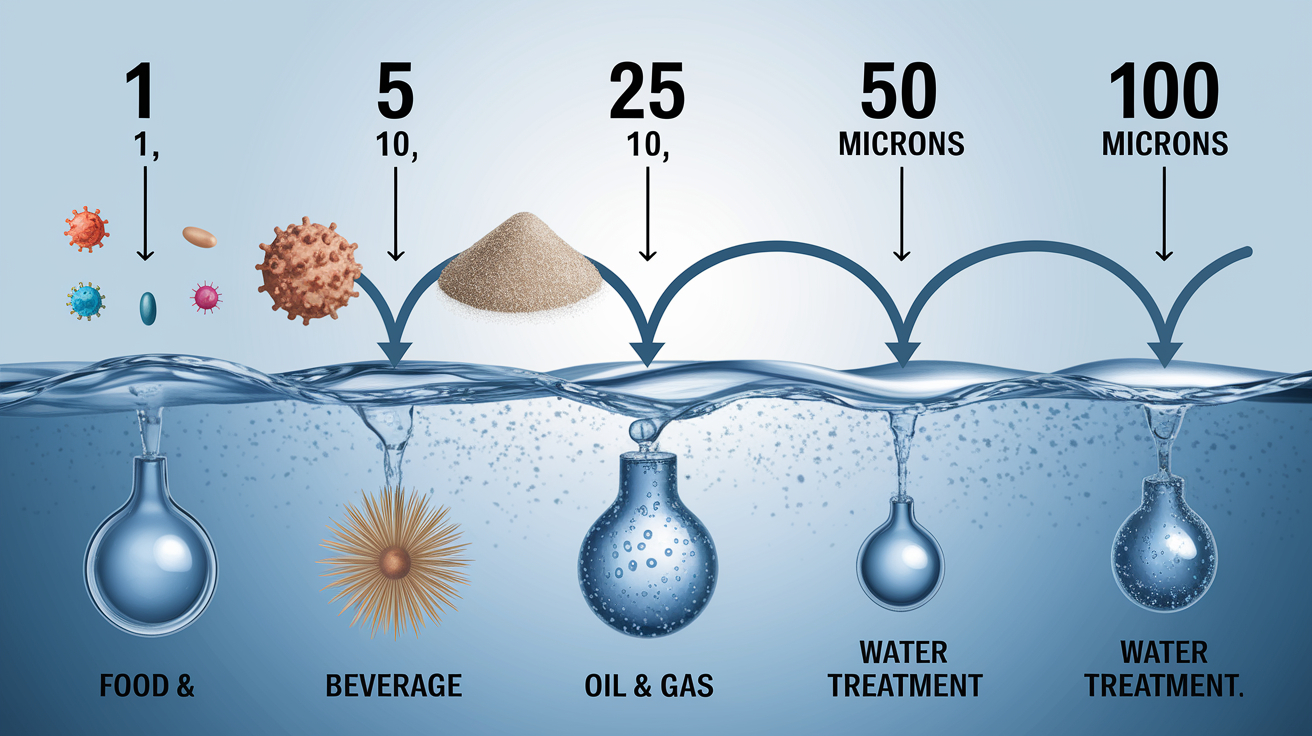
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
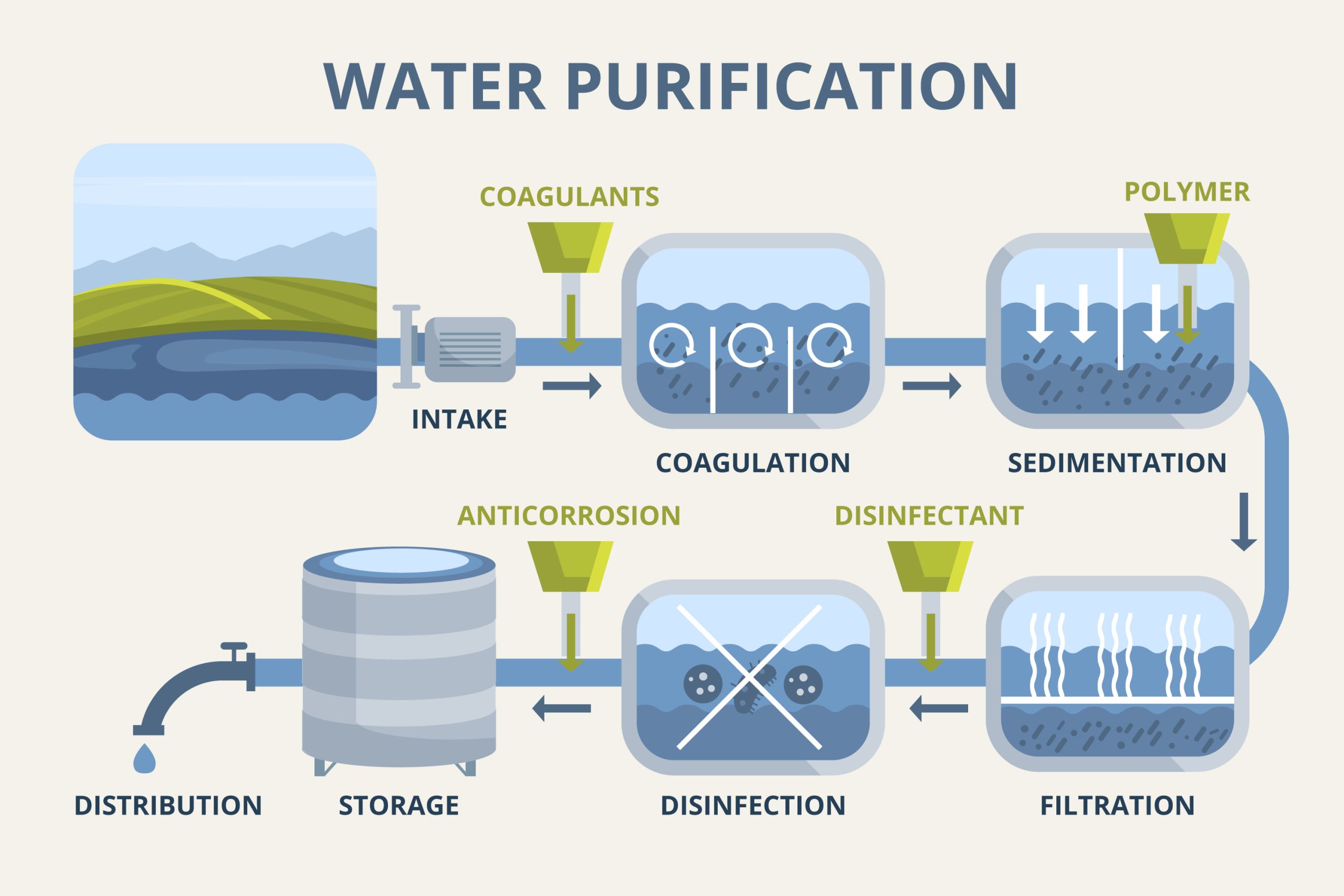
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



