

A butterfly valve is a flow-regulating device used to control, start, slow, or stop the flow of media through a pipeline. Its disc remains in the flow path, impacting pressure, and it operates through a simple quarter-turn mechanism. This article explores the types, applications, and benefits of butterfly valves.
Key Takeaways:
- Butterfly valves are efficient flow control devices, characterized by their lightweight design and quick actuation, making them suitable for various applications including water supply and industrial processes.
- There are three primary types of butterfly valves—zero offset, double offset, and triple offset—each offering unique sealing mechanisms and pressure tolerances for specific operational needs.
- Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of butterfly valves, ensuring they continue to operate efficiently in various fluid control environments.
Butterfly valves are essential components in regulating the flow of fluids through pipelines. Named for their distinctive wing-like movement, these valves are designed to control, start, slow, or stop media flow efficiently. Unlike other valve types, the disc of a butterfly valve is always in the flow path, which affects pressure at any position. This unique feature sets them apart from ball valves and gate valves.
One of the key advantages of butterfly valves is their lightweight nature, which makes them suitable for a wide range of applications without adding significant weight to the system. This feature not only reduces installation costs but also minimizes labor, equipment, and piping support requirements.
Butterfly valves operate through the rotation of a valve disc, which can be positioned either parallel or perpendicular to the flow of media. When the valve is open, the disc is set perpendicular to the flow direction, allowing fluid to pass through freely. This quarter turn valve mechanism enables quick and efficient flow control.
In the closed position, the disc blocks the valve bore, preventing fluid flow. The design of butterfly valves often includes a double eccentric disc, which helps maintain an unstressed sealing ring in the open position, ensuring a tight shutoff and minimal wear on the components.
Disc: The central component that regulates fluid flow, rotating to either allow or restrict passage. Its design plays a crucial role in achieving tight shutoff and minimal wear.
Rod: Connects the disc to the actuator, enabling the transfer of motion necessary for opening or closing the valve. It must be durable to withstand operational stresses.
Actuator: Provides the force required to move the disc, available in manual, electric, or hydraulic forms. This component is essential for precise control and automation in various applications.
Valve Body: Available in wafer style, lugged, and double-flanged configurations, each offering unique installation advantages. The choice of body type depends on the specific application and installation scenario.
Seating Options: Includes metal, soft-seated, or rubber-lined choices, tailored to specific application requirements. The seating ensures a tight closure for efficient flow control.
Sealing Rings: Located on both the upstream and downstream ends to prevent leaks and maintain efficient operation. These rings are vital for ensuring reliable performance in diverse conditions.
Butterfly valves can be actuated through various methods, including manual, electric, and hydraulic actuation. Each method offers unique advantages, making them suitable for different applications and operational requirements.
Manual actuation is advantageous due to its ease of installation and maintenance, relying on straightforward mechanics. These valves are highly reliable as they avoid complications associated with mechanical or electrical failures. However, manual actuation requires more physical effort and is less efficient for rapid operations.
Electric actuators enhance butterfly valves’ functionality by providing precise control and automation capabilities.
Electric actuators reduce the need for manual intervention, allowing remote control and integration with automated systems. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high precision and efficiency in electric actuator fluid flow control.
Hydraulic actuators provide the necessary force for heavy-duty applications, enabling butterfly valves to handle high-pressure and high-flow situations effectively. The use of hydraulic power ensures efficient control of valve operations, especially in demanding industrial environments.
Butterfly valves with hydraulic actuation are favored for their lightweight design and ability to operate in confined spaces. This makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications where space and force requirements are critical.
Butterfly valves are categorized into three primary types: zero offset, double offset, and triple offset. Each type offers distinct features and benefits, making them suitable for specific applications and operating conditions.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right valve for your needs.
Zero offset butterfly valves, also known as concentric or rubber-seated valves, are designed to create a tight seal by deforming the soft seat with the disc during operation. This type of valve achieves sealing through interference. This occurs along the disc edge at the stem, where the disc meets the disc seat. They are ideal for general-purpose applications with a pressure rating of up to 250 PSI and can withstand temperatures up to 400°F.
However, zero offset butterfly valves have the lowest pressure rating among the three types, limiting their use in high-pressure environments. Despite this limitation, they are a cost-effective solution for many low to medium pressure applications.
Double offset butterfly valves, or double eccentric valves, feature an offset in two places, increasing the durability of the seal. These high-performance valves can tolerate pressures up to 1440 PSI, with pressure ratings available at PN 10 and PN 16. Their design allows them to accommodate higher temperatures, making them suitable for high pressure systems applications.
The disc of a double offset butterfly valve functions like a gate valve to stop or throttle fluid flow, with design variations that enhance flow performance. This makes them a versatile choice for many industrial settings where durability and performance are critical.
Triple offset butterfly valves are designed with three offsets, creating a cam action that provides right-angled conical sealing and frictionless, long-wearing seals. These valves can tolerate temperatures up to 1200°F, making them ideal for high-heat applications. Additionally, they have a maximum pressure tolerance of 1,480 PSI, ensuring reliable performance under high-pressure conditions.
The triple offset design minimizes wear and tear, offering a durable solution for demanding environments. Their advanced sealing capabilities make them the go-to choice for applications requiring the highest level of performance and longevity, thanks to the zero offset design.
Butterfly valves offer numerous advantages, including versatility, cost-efficiency, and compact design. These benefits make them a preferred choice for various fluid control applications across different industries.
One of the standout features of butterfly valves is their compact design. Compared to standard gate valves, butterfly valves occupy significantly less space. Their lower footprint requirement makes them ideal for installations with limited space.
The compact nature of these valves also translates to reduced raw material usage, lower energy consumption for transport, and easier installation and maintenance. This makes them a practical and efficient choice for many applications.
Butterfly valves are typically more cost-effective compared to other valve types. Their simpler design results in lower procurement costs, making them a budget-friendly option for many applications. Despite possible higher installation costs, the overall maintenance and operational savings can lead to a lower total cost of ownership over time.
The manufacturing simplicity of butterfly valves reduces production costs, which is particularly beneficial for larger installations. This cost efficiency is one of the key reasons for their widespread use in various industries.
Butterfly valves are known for their versatility in handling various types of fluids across different pressures. Their design allows them to be used in diverse applications, from water supply to industrial processes. This versatility translates into enhanced efficiency and reliability in various operational contexts.
The quick operation enabled by hydraulic actuators makes them ideal for situations demanding rapid response. This adaptability and efficiency make butterfly valves a valuable asset in many fluid control systems.
Regular maintenance is vital to ensure butterfly valves operate efficiently and have a long service life. One of the best practices is to cycle the valve at least once a month to prevent operational issues. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear or damage, ensuring that the valve remains in proper working condition.
For valves used in dry applications, regular lubrication of the disc and seat is necessary to extend their lifespan. Additionally, lubricating the stem and other moving parts periodically will prevent sticking and ensure smooth operation. Seals within the valve should be checked regularly to maintain a tight closure and prevent leakage during operation.
Butterfly valves are a versatile and efficient solution for fluid control across various industries. They offer many advantages, including a compact design, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to handle diverse fluids and pressures. Understanding the different types of butterfly valves—zero offset, double offset, and triple offset—enables better selection for specific applications.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial to ensuring that butterfly valves perform optimally and have a long service life. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this guide, you can maximize the benefits and reliability of butterfly valves in your system.
The main types of butterfly valves are zero offset, double offset, and triple offset, each tailored to specific pressure and temperature requirements. Understanding these options can help you select the appropriate valve for your application.
Butterfly valves function by rotating a disc to control fluid flow; the disc’s position can be adjusted to be either parallel or perpendicular to the flow, allowing for efficient regulation with a quarter-turn mechanism.
The key components of a butterfly valve are the disc, rod, actuator, and the valve body, which is often constructed from ductile iron and coated with epoxy powder. Various seating options are available to suit different applications.
Butterfly valves provide significant benefits such as a compact design, cost-effectiveness, and versatility for managing different fluids and pressures. These features make them an efficient choice for various applications.
To ensure the longevity and proper functionality of butterfly valves, it is essential to perform regular cycling, inspect for wear and damage, and periodically lubricate the disc, seat, and stem. These maintenance practices will optimize the valve’s performance and reliability.

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
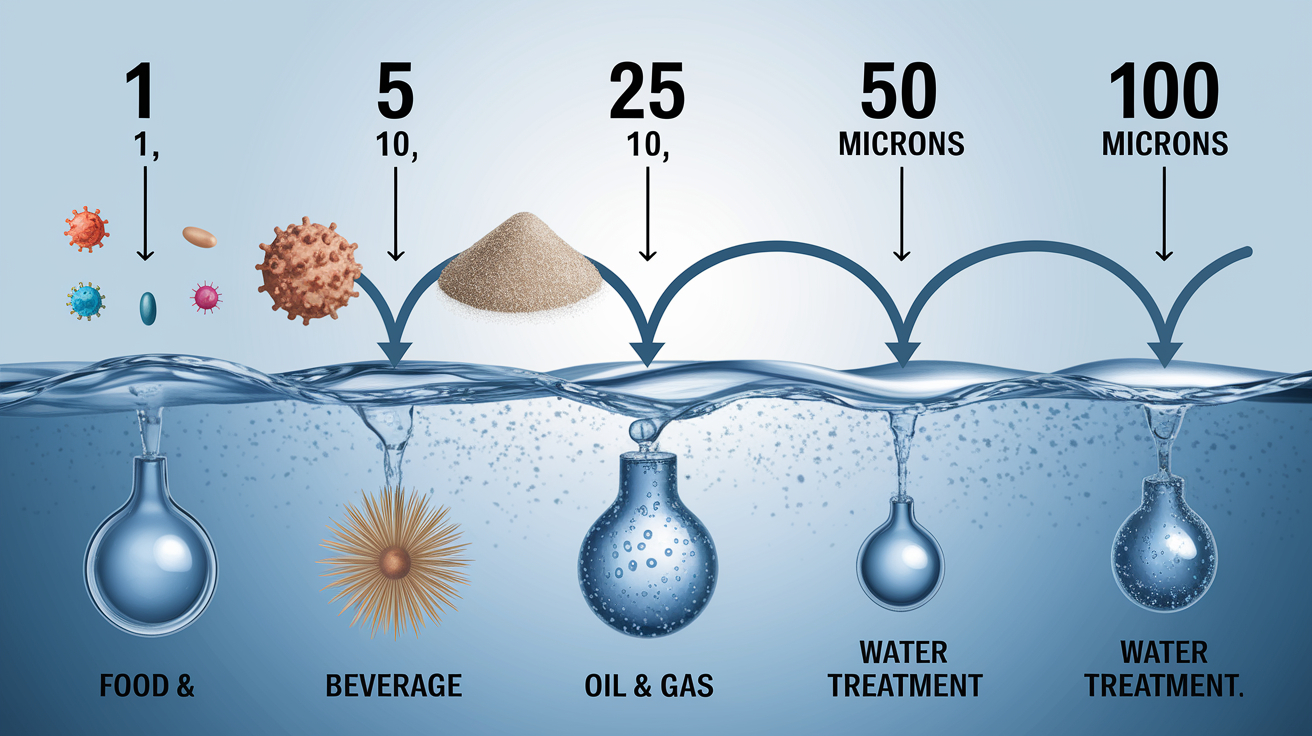
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
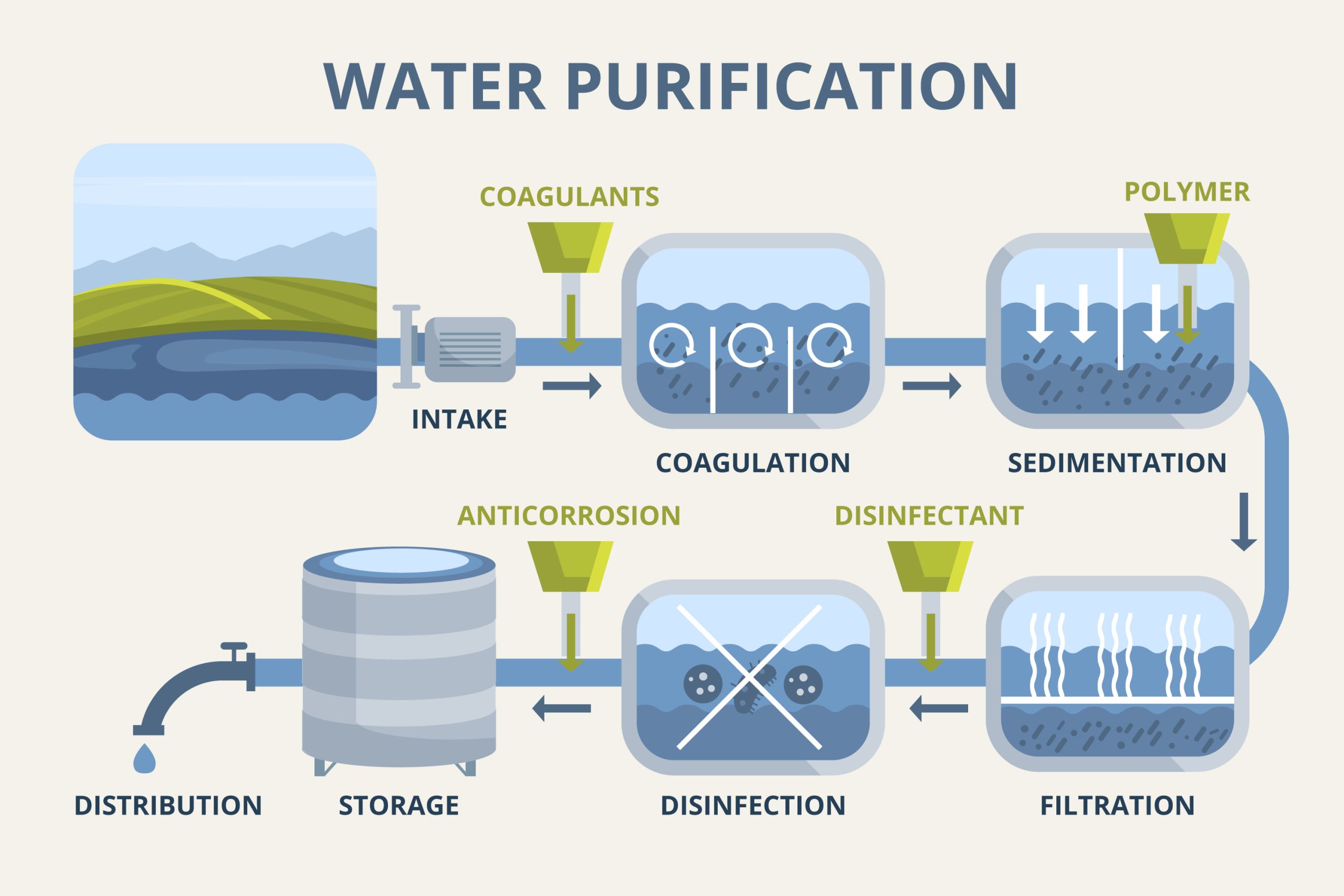
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



