

Strainers in piping systems work by filtering out impurities — safeguarding both the quality of the fluid and the efficiency of the system.
In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and food production, piping systems are essential for transporting fluids like liquids, gases, and slurries.
These fluids often carry unwanted solid particles or debris that can damage equipment and clog pipelines. This is where strainers play a vital role in protecting the system.
That’s why choosing the correct type of pipe strainer ensures smooth operation and prevents costly downtime due to contamination or equipment failure.
With various types of strainers available, understanding their functions and selecting the appropriate one for your application can be challenging.

In this article, we’ll cover the basics of strainers, their types, and factors to consider when selecting the right strainer for your system.
A strainer is a device that removes solid particles, debris, and impurities from fluids in a piping system.
It consists of a perforated or mesh screen that traps unwanted particles while allowing the fluid to pass through.
Strainers are essential in many industries, including oil and gas, chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing, where they maintain product quality, prevent equipment damage, and ensure the overall efficiency of the system.
In piping systems, strainers act as filters, preventing harmful particles from entering and damaging downstream equipment like pumps and valves. They also help ensure that the final product remains free of contamination.
There are several types of strainers used in piping systems. Choosing the right type depends on factors such as the flow rate, pressure, and the size of particles that need to be filtered.
Let’s explore the different types of strainers commonly used:
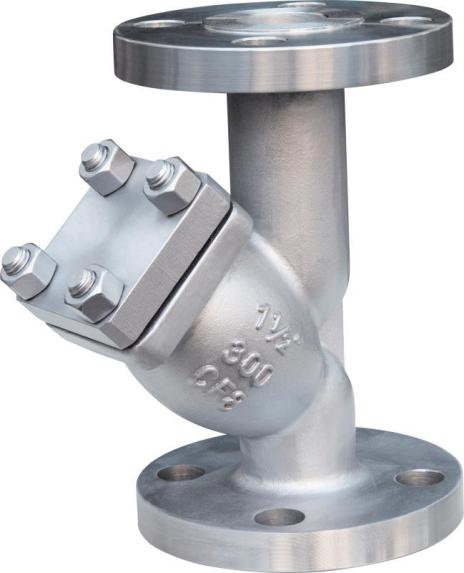
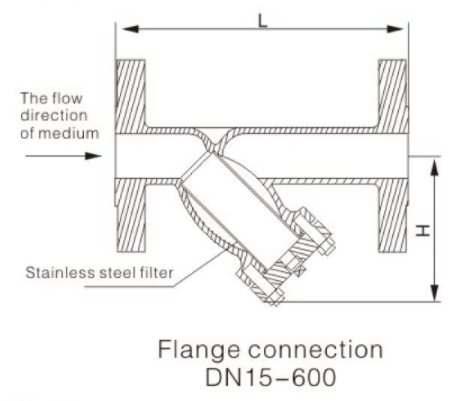
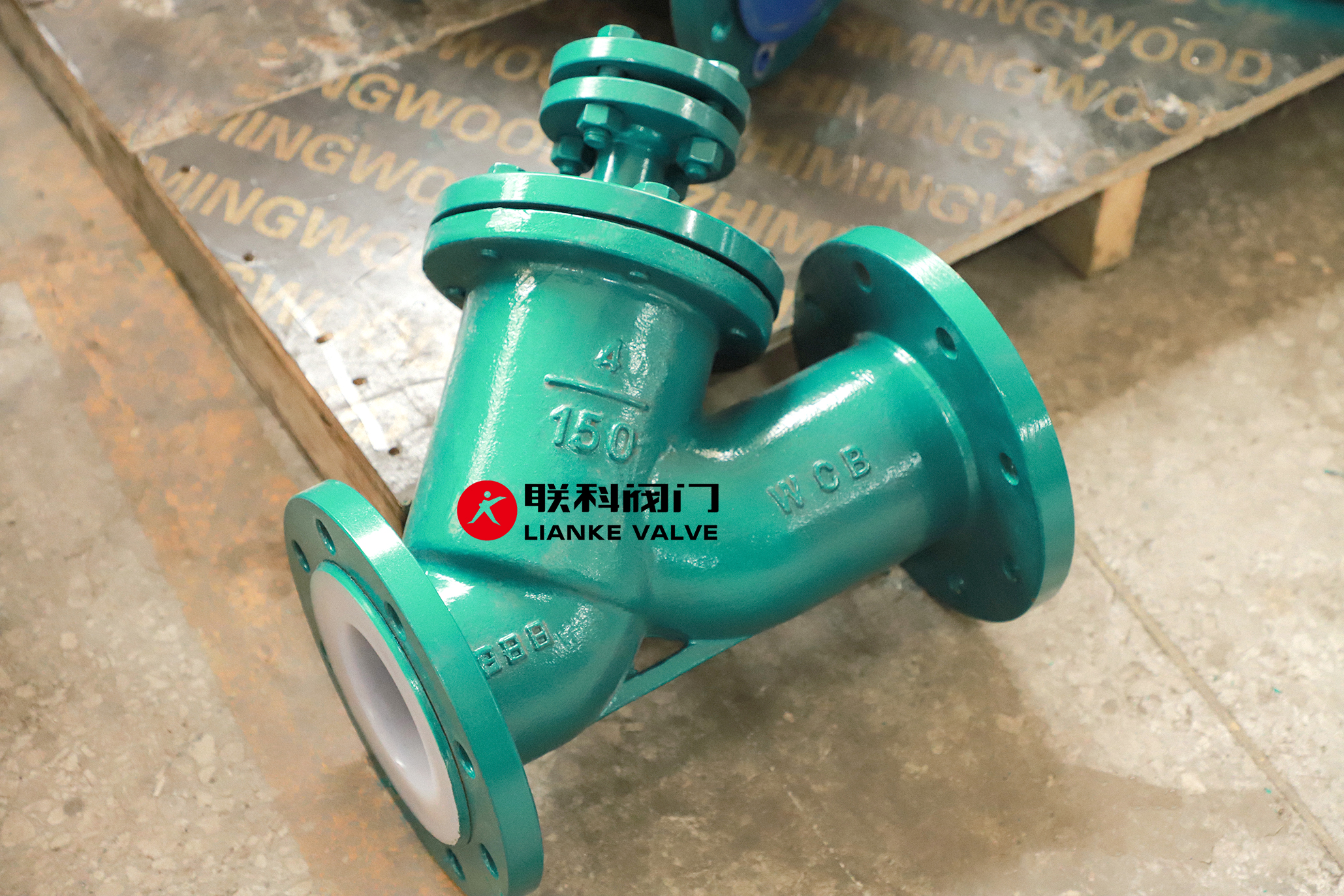
The Y-type strainer is one of the most widely used strainers due to its versatility and ability to filter small particles.
Named after its Y-shaped design, the Y-strainer valve is typically used in pipelines with high-pressure levels where even small amounts of debris can cause damage.
It is suitable for both horizontal and vertical installations, although it is often recommended for vertical setups to minimize erosion.
A flanged Y strainer is a common variant used in applications requiring easy maintenance access.
It allows for quick cleaning or replacement of the strainer screen without disassembling the entire system.
This type of strainer is ideal for protecting sensitive equipment in high-pressure pipelines, such as pumps and control valves.
However, Y-type strainers are not designed to handle large amounts of dirt and debris, so they require regular maintenance to prevent clogging.

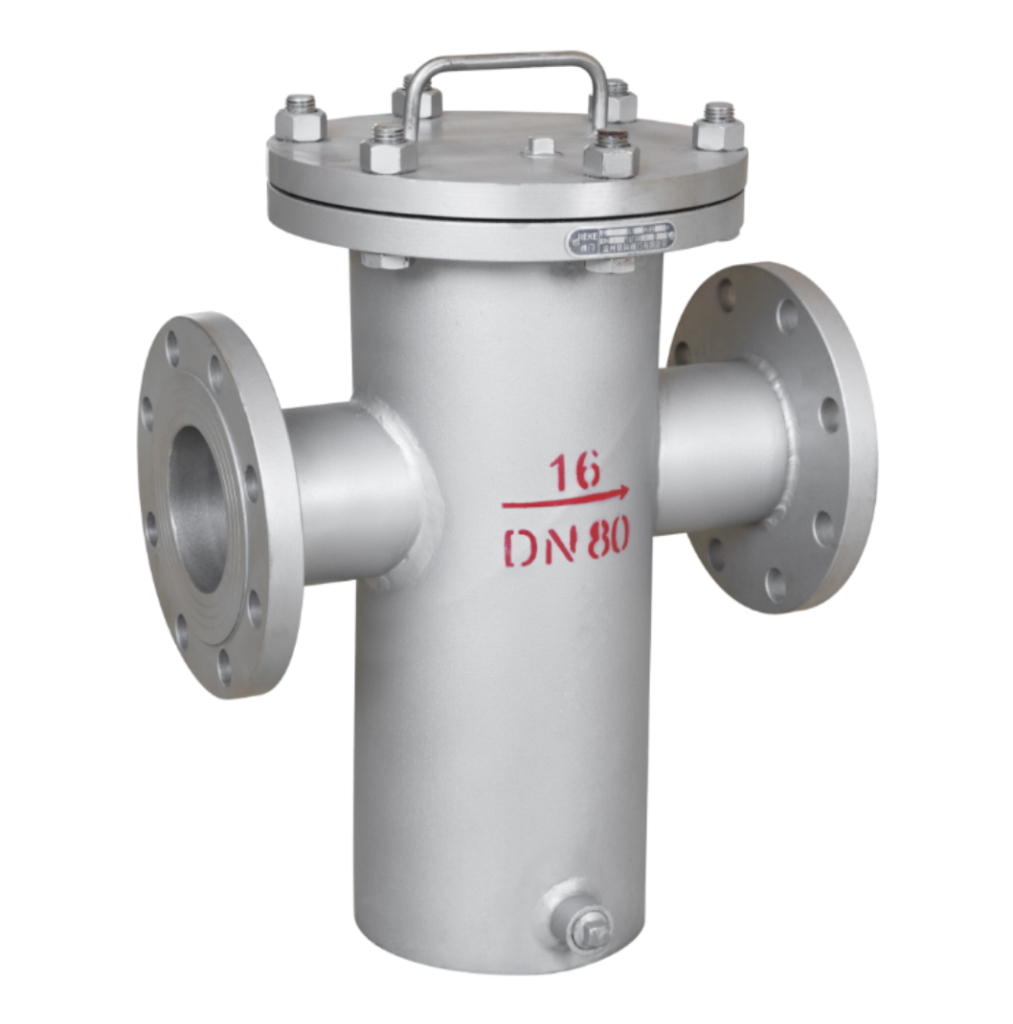
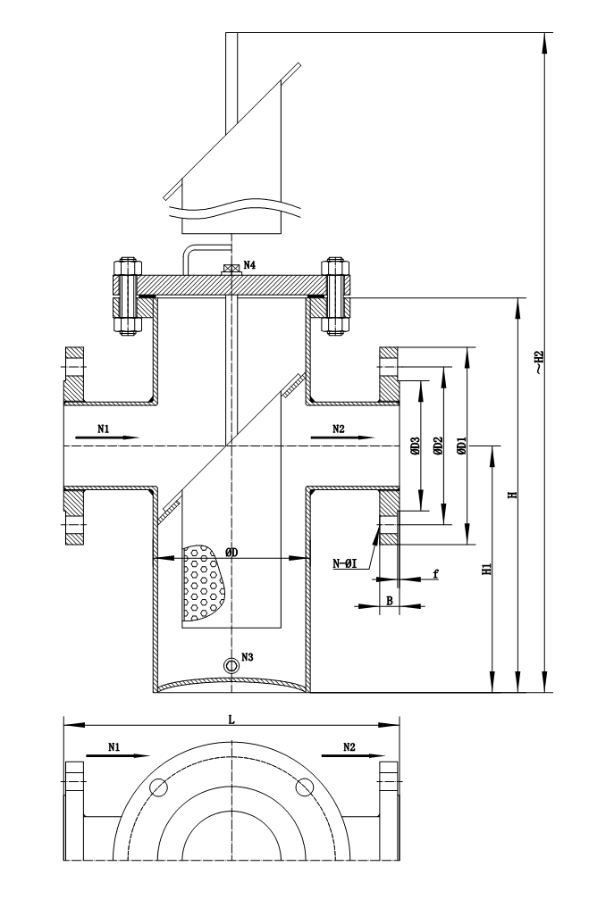
Basket strainers are another common type of strainer, designed to filter out larger particles than Y-strainers.
They feature a larger surface area, which allows them to trap more debris and reduce the frequency of cleaning.
Basket strainers are typically used in applications with a maximum pressure of around 1,500 PSI and are installed in parallel pipes.
The advantage of basket strainers is their ability to hold more debris before needing cleaning, making them ideal for pipelines that experience higher volumes of contaminants.
They can be easily cleaned by removing the top cover, which provides direct access to the straining element.

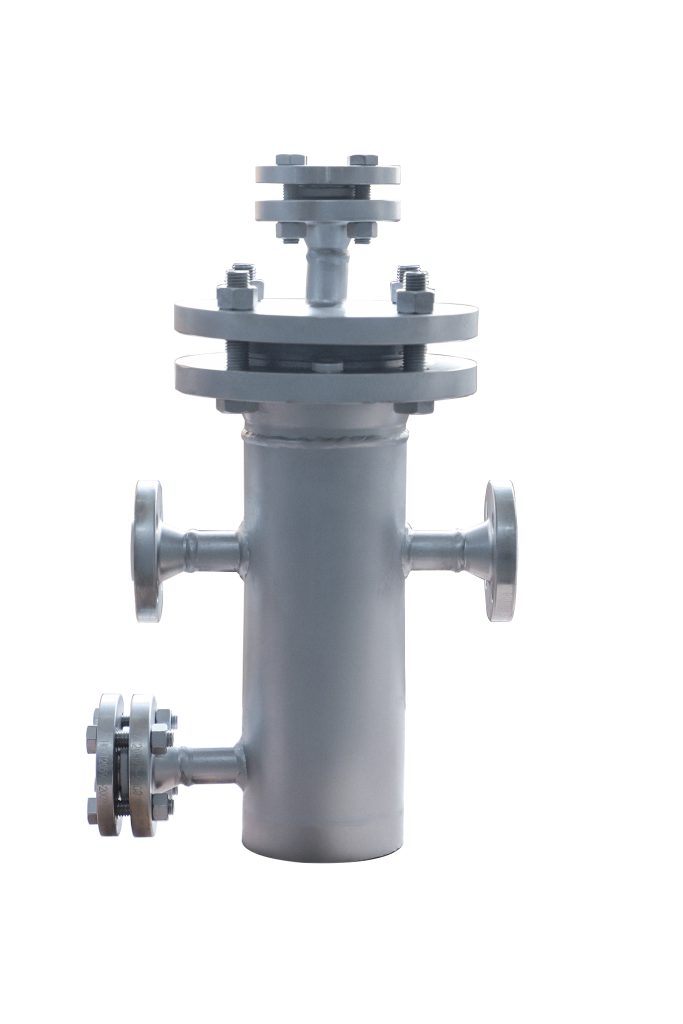
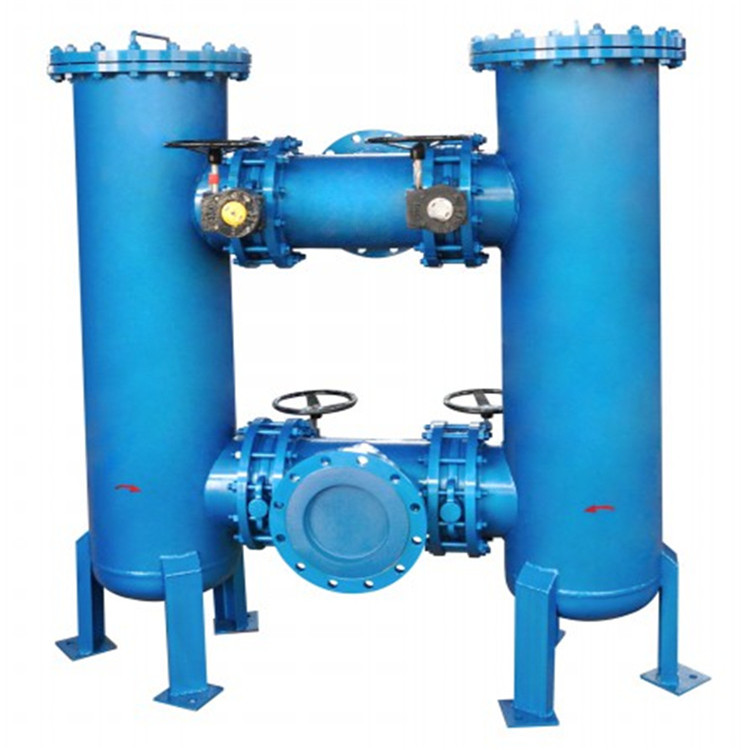
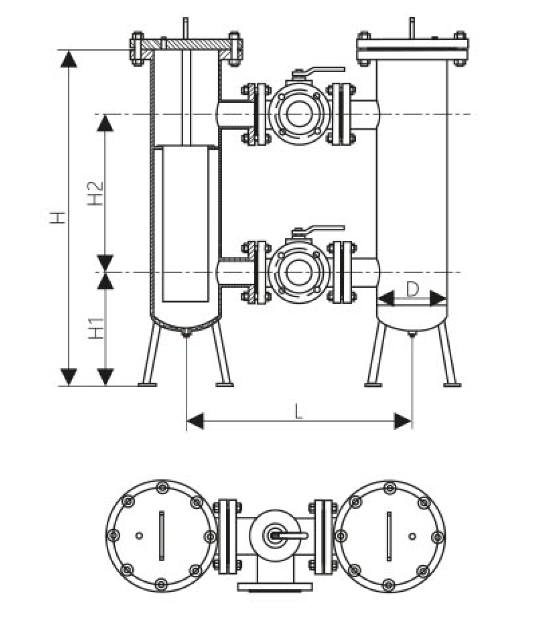
Duplex strainers are designed for continuous operation, making them ideal for systems that cannot afford downtime for maintenance.
These strainers consist of two filtering elements, one of which remains in operation while the other is cleaned or replaced.
When one strainer becomes full, the flow is redirected to the other, ensuring uninterrupted filtration.
Duplex strainers often come with a plug or ball-type valve that allows for easy switching between the two straining elements.
They are best suited for applications where continuous flow is required, such as in the oil and gas or chemical industries.

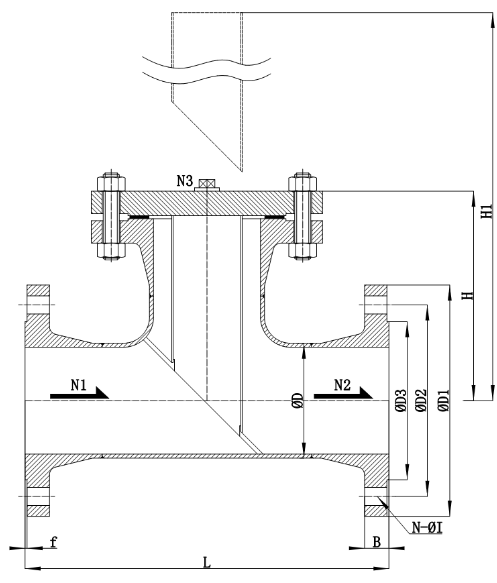
As the name suggests, temporary strainers are used for short-term applications, typically during system start-up to protect equipment from initial debris or contaminants.
These strainers are usually cone-shaped or flat and are installed between flanges. They are often removed once the system has been fully flushed and cleaned.
Temporary strainers are cost-effective and provide excellent protection during the initial phases of operation, but they are not intended for long-term use.
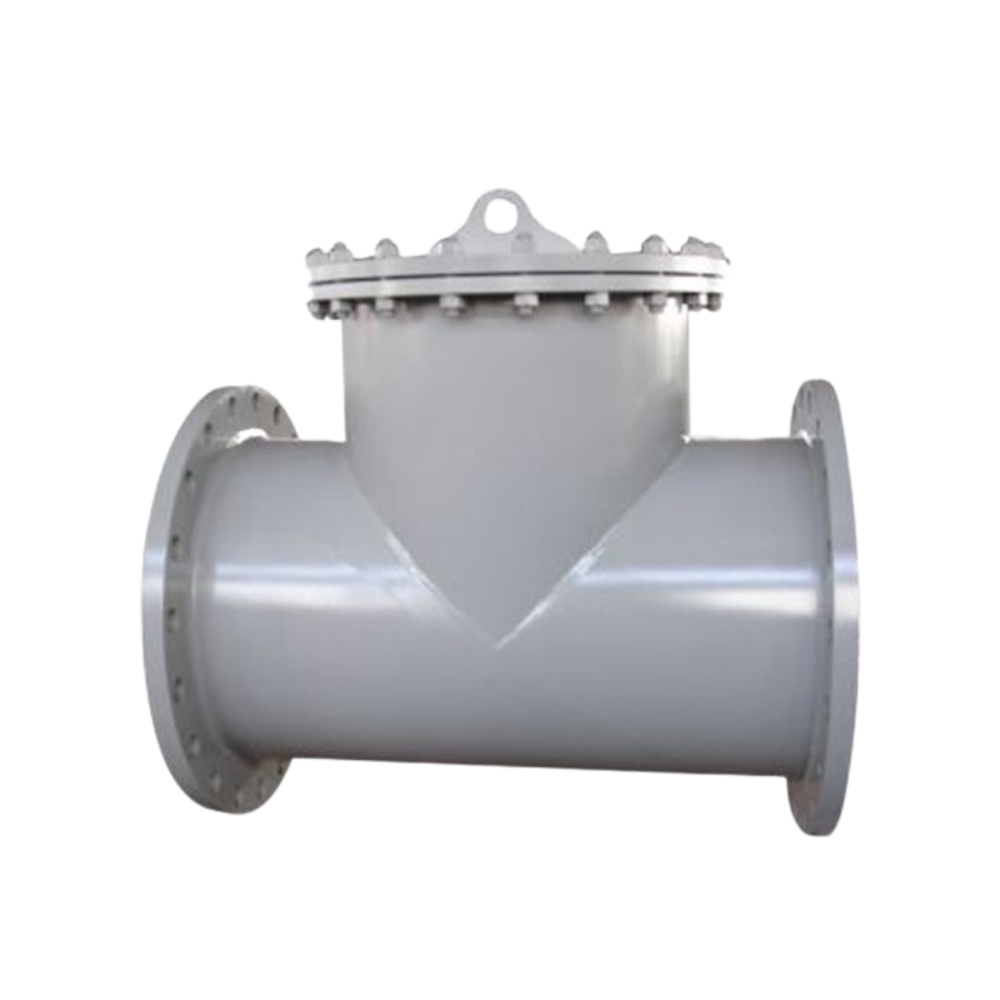
Cone strainers, also known as “T-strainers” or “Tee strainers,” are used in low-pressure applications where space is limited.
Their conical shape provides a large filtration area, making them highly effective at trapping solid particles and reducing the frequency of maintenance.
These strainers are typically installed vertically and are suitable for applications that require a high level of filtration.
Cone strainers are ideal for systems that cannot accommodate larger strainer types and where the flow rate is moderate to low.
They offer an excellent balance between filtration efficiency and space-saving design.

When selecting a strainer for your piping system, there are several important factors to consider. These factors help ensure that you choose the right strainer for your specific needs:
The strainer should match the flow rate of your system to avoid pressure drop issues. Strainers that cannot handle the flow rate of your system will clog quickly and require frequent cleaning.
The strainer must be able to withstand the system’s operating pressure without causing leaks or failures.
For high-pressure applications, a flanged strainer may be more appropriate, as it provides a secure and durable connection.
Ensure that the strainer can handle the temperature of the fluid without degrading. Materials like stainless steel are often used in high-temperature applications to prevent corrosion and deformation.
Different strainers are designed to filter particles of specific sizes. Y strainers, for example, typically filter smaller particles, while basket strainers can handle larger debris.
Choosing the right mesh size ensures effective filtration and prevents damage to downstream equipment.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep strainers functioning effectively.
Consider how often the strainer will need to be cleaned and whether your system can accommodate downtime for maintenance.
Duplex strainers are ideal for systems that require continuous operation.
Choosing the right strainer for your piping system is essential for maintaining system efficiency, protecting downstream equipment, and ensuring product quality.
From Y-type strainers and basket strainers to duplex strainers and cone strainers, each type serves a specific purpose.
Understanding the flow rate, pressure, temperature, and particle size requirements of your system will help you make an informed decision.
By selecting the appropriate pipe strainer manufacturer, you can ensure the smooth operation of your system, reduce maintenance costs, and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
Whether you’re working in oil and gas, food processing, or chemical industries, choosing the right strainer is critical to maintaining a safe and efficient piping network.
Resources:
The Ultimate Guide to Types of Strainers in Piping: Which One is Right for You
101 Guide on Different Types of Strainers in Pipeline

ANSI Class Ratings for Y strainer flanges tell you how much pressure and temperature the flange can handle. These ratings help you choose the right flange material and design to keep your piping system safe and efficient. If you’re installing or replacing a Y strainer in a pipeline, understanding ANSI ratings isn’t optional—it’s essential. Choosing […]

To choose the right wye strainer, you need to understand mesh and screen size. These determine what particles your system can filter out. The finer the mesh, the smaller the particles it catches. This guide explains how to select the correct strainer mesh size, use a mesh size chart, and compare mesh size vs micron […]
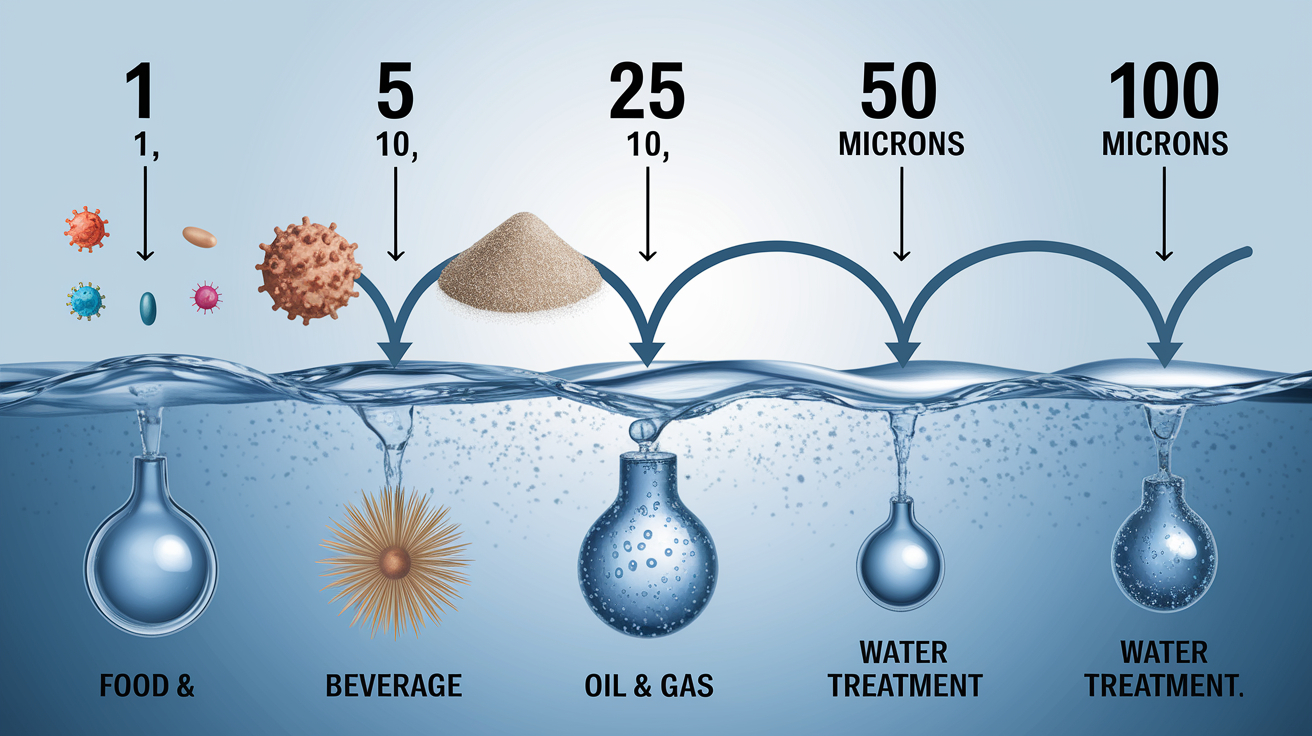
When choosing a filter or strainer for your system, micron ratings tell you how small the particles are that your filter can catch. In simple terms, the smaller the micron rating, the finer the filter. Whether you’re in water treatment, chemical processing, or any industry that relies on micron filtration, knowing the right micron size […]
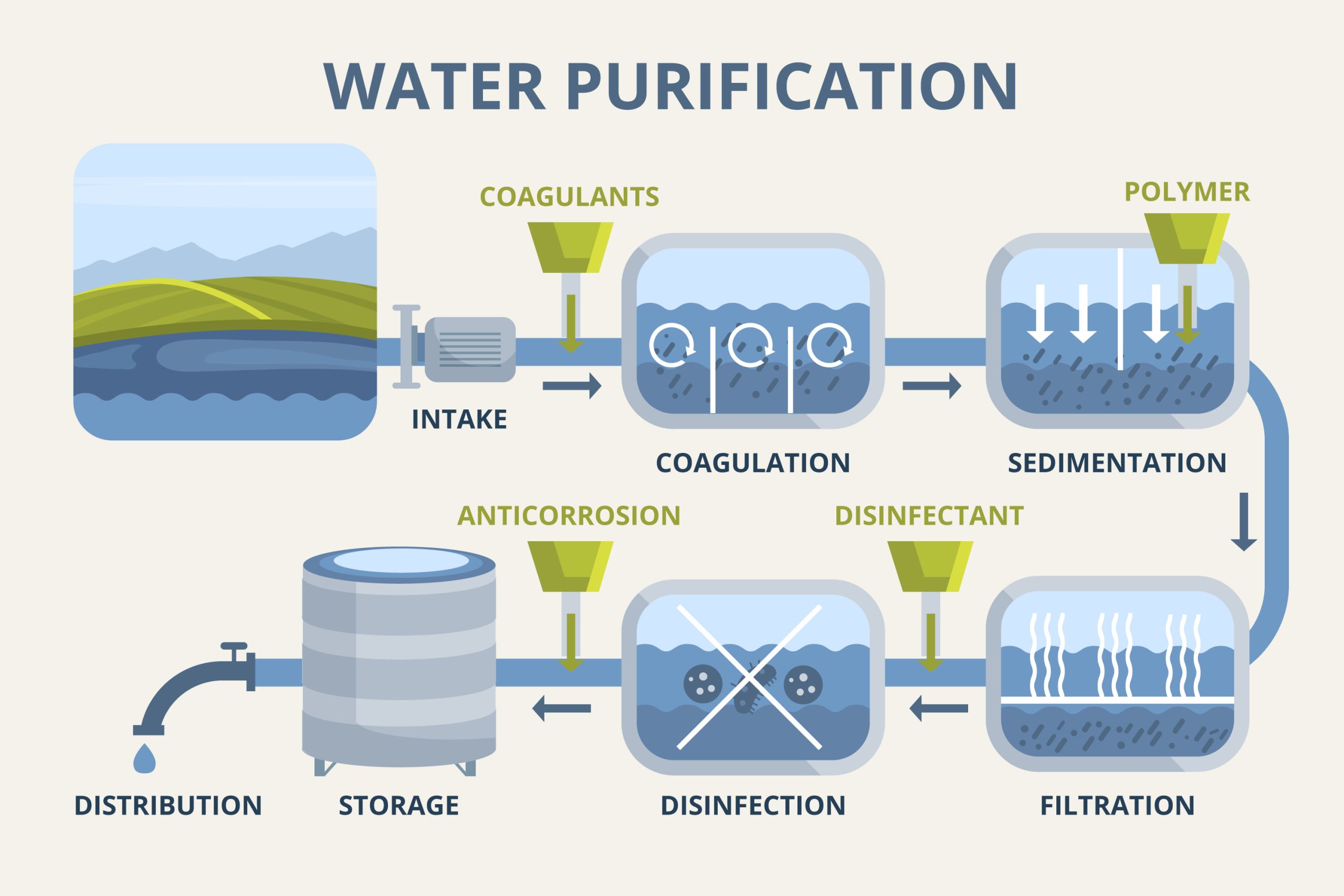
Municipal water doesn’t just show up clean at the tap—it’s the result of a carefully managed process. The liquid filtration process for municipal water treatment plants is the backbone of safe, clean drinking water. From removing dirt and debris to eliminating harmful pathogens, each step in this system ensures water meets strict safety standards. In […]



