

In industrial systems, check valves are critical for preventing backflow, protecting equipment, and maintaining process efficiency. However, improper installation can lead to premature wear, leaks, or even system failure. For engineers, mechanics, and technicians, understanding the technical nuances of check valve installation is essential. This guide breaks down key considerations, supported by industry standards and data, to ensure your valves perform reliably under demanding conditions.
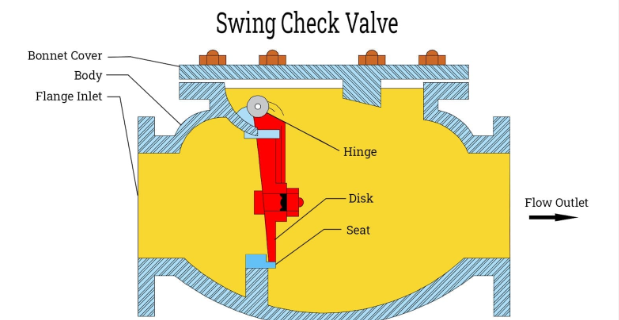
Check valves are simple devices, but their effectiveness hinges on precise installation. Here’s what you need to prioritize:
Position check valves where they’re easily accessible for inspection and maintenance. For example, isolating a pipeline section during repairs requires valves to be strategically placed—ideally near pumps, elbows, or system branches. According to Rangeline, valves installed too close to bends or fittings risk turbulence, which accelerates wear.
Key Rule:
This minimizes turbulent flow, reducing stress on the valve disc and seat.
Check valves must align with the system’s flow direction. The valve body typically has an arrow indicating the correct orientation. Gravity-dependent valves (e.g., swing check valves) require vertical installation with flow moving upward. In contrast, silent spring-loaded check valves work in any orientation, including horizontal lines (Milwaukee Valve).
Pro Tip: After installation, verify the valve opens freely in the flow direction. A stuck disc can cause dangerous pressure surges.
The valve’s connection method impacts durability and leak resistance. Below is a comparison of common types:
| Connection Type | Best Applications | Pressure Rating | Ease of Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threaded | Low-pressure systems (e.g., water lines) | Up to 150 psi | Simple, but prone to leaks if overtightened |
| Flanged | High-pressure, high-temperature systems | 150–2500 psi | Easy disassembly, requires precise alignment |
| Welded | Permanent, high-integrity systems (e.g., chemical plants) | 2500+ psi | Permanent; no disassembly possible |
Source: Rangeline, Allied Valve
Flanged connections are ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance, while welded joints suit corrosive or high-pressure environments.
Follow these steps to ensure a secure, leak-free installation:
Valve materials must withstand the fluid’s chemical properties and temperature. For example:
Always cross-reference the valve’s pressure-temperature rating with the system’s operating conditions (Tameson).
Over-tightening threaded connections can strip threads or crack the valve body. For NPT threads, tighten until snug, then add 1/4 to 1/2 turn with a wrench.
Proper check valve installation isn’t just about following steps—it’s about understanding how design, placement, and materials impact long-term performance. By adhering to straight-pipe guidelines, choosing the right connection type, and verifying flow direction, you’ll minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
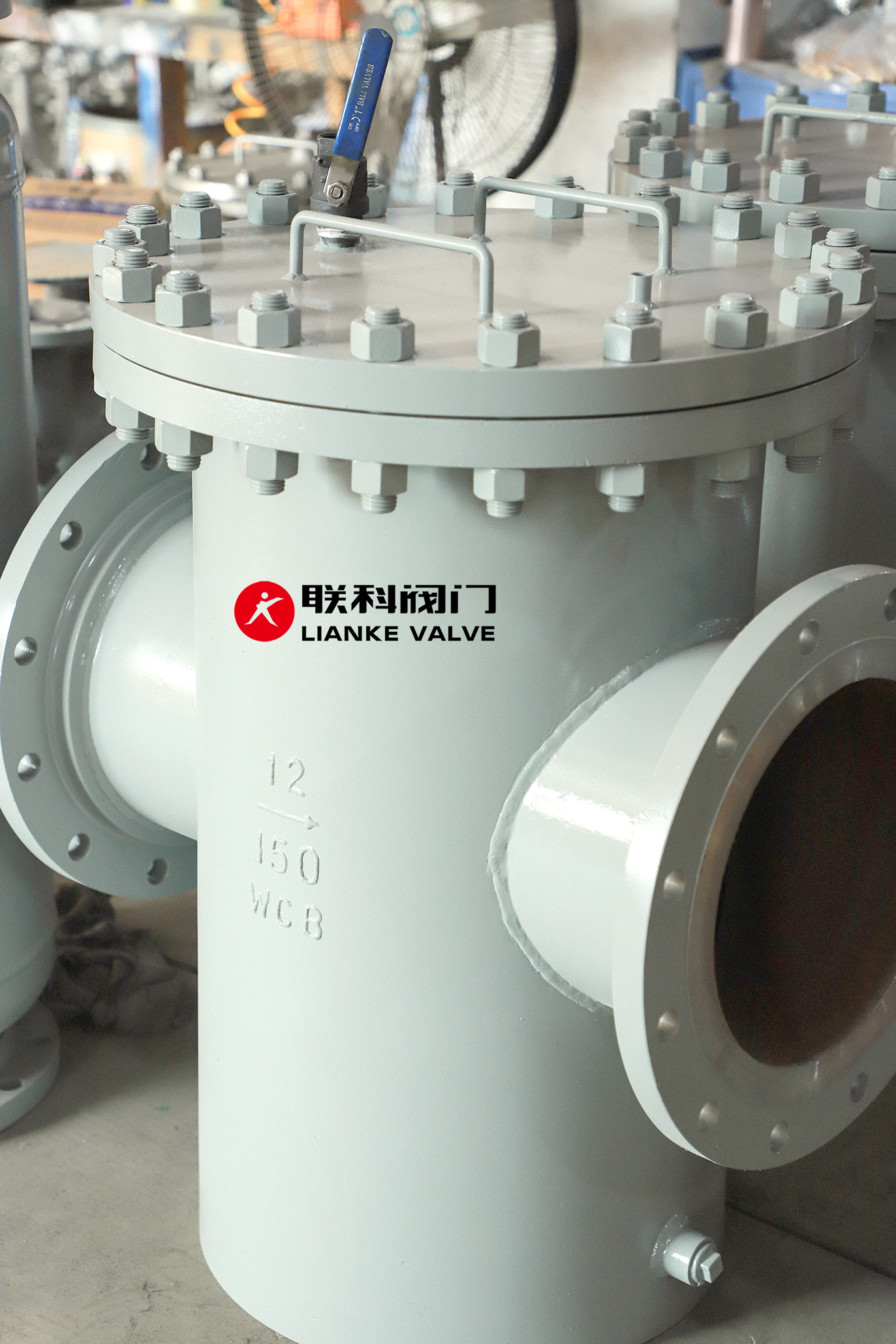

Choosing the right basket strainer for your system comes down to understanding filtration size, strainer mesh, and how these elements fit into your specific piping setup. Whether you’re working in chemical processing, food production, water treatment, or HVAC, the right strainer ensures system protection, flow efficiency, and long-term equipment performance. This article will help you […]
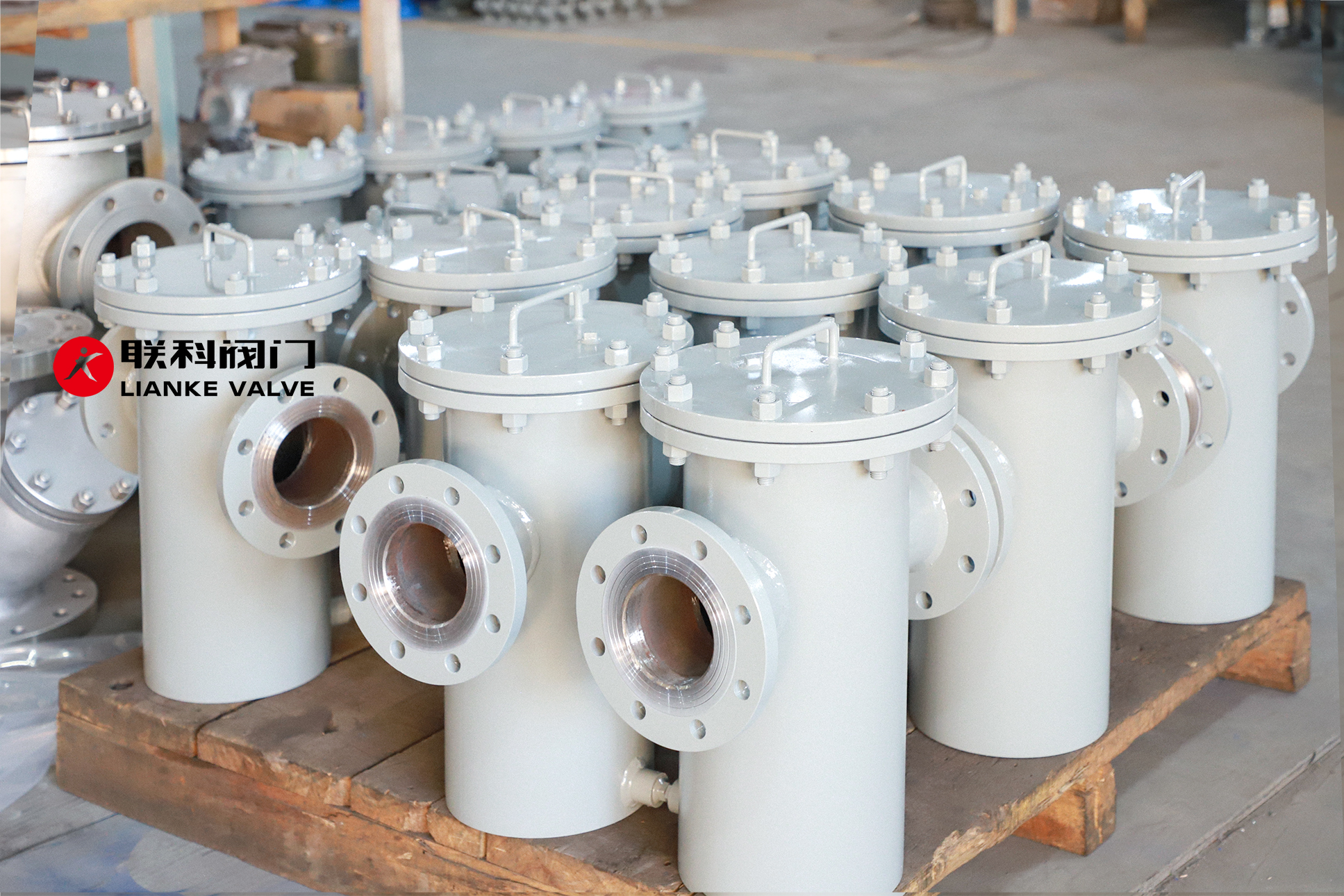

Installing, operating, and maintaining a basket strainer properly ensures optimal system performance, protects downstream equipment, and extends the life of your filtration system. Whether used in chemical processing, HVAC, food production, or water treatment systems, basket strainers are essential components for removing solid particles from fluids. In this article, we’ll break down the complete lifecycle […]
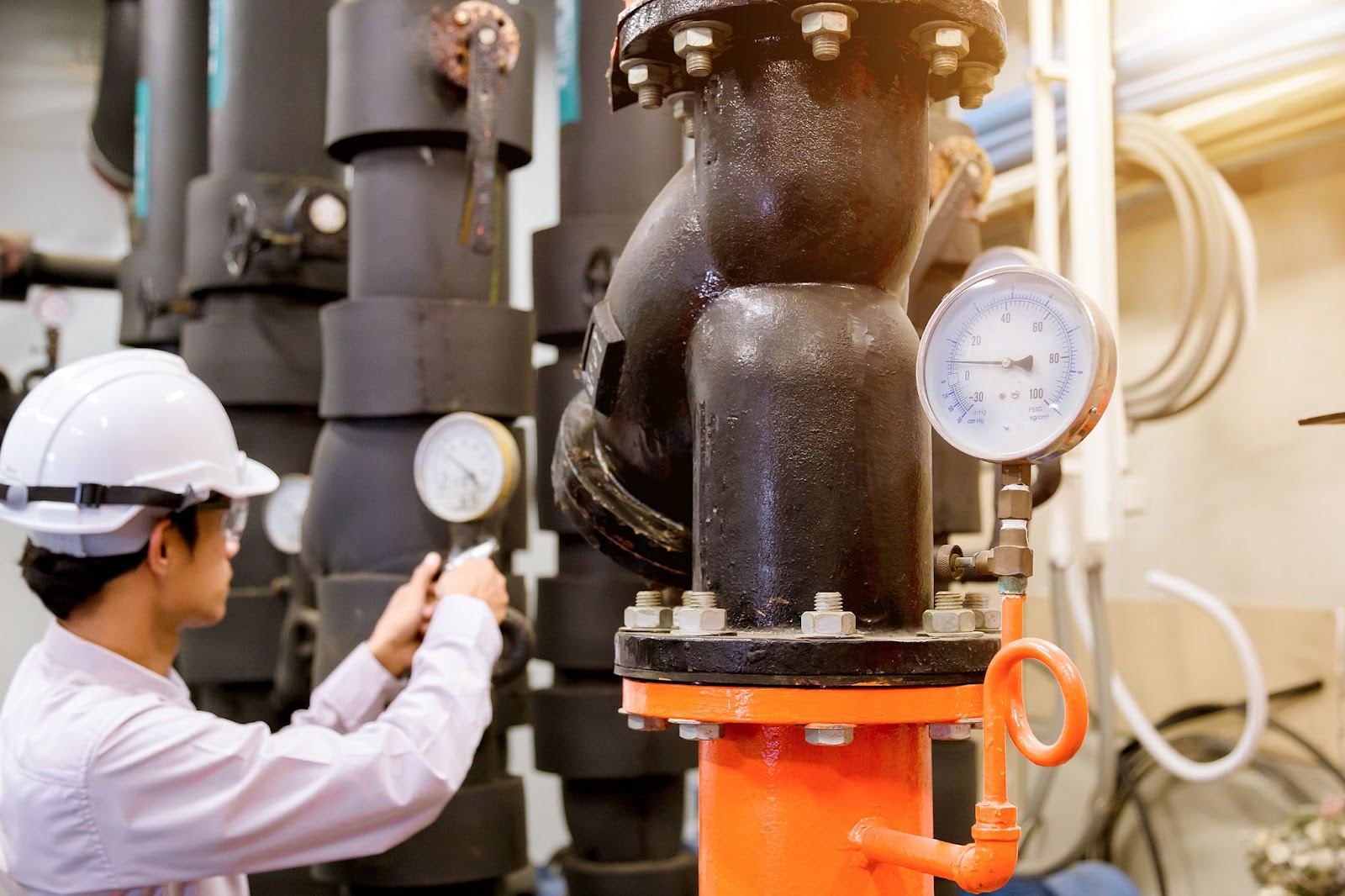

Valve testing ensures that industrial valves meet strict performance, safety, and durability standards before they are installed in real-world systems. This process verifies that valves operate reliably under pressure, prevent leaks, and perform in extreme conditions such as high temperature or cryogenic environments. Whether it’s a valve leak test or a gas valve test, the […]

The most effective way to resolve pinch valve issues is to identify the root cause early—whether it’s sleeve wear, actuation failure, or leaks—and apply targeted troubleshooting steps to restore performance. Pinch valves are favored for their durability and simplicity in handling slurries, abrasive materials, and corrosive fluids. But like any component, they can develop problems […]



